Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2024; 30(15): 2155-2174
Published online Apr 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i15.2155
Published online Apr 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i15.2155
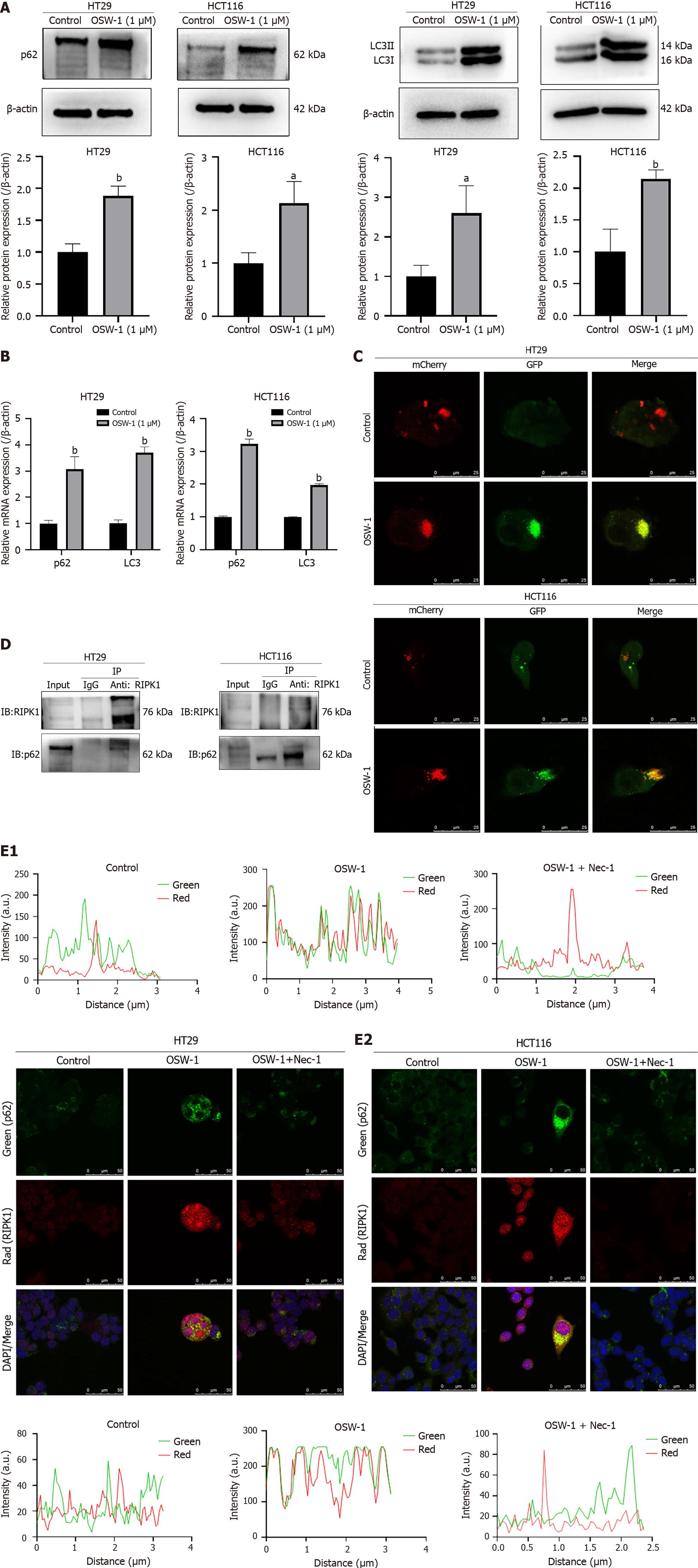
Figure 5 Impairment of the autophagic flux results in the accumulation of p62/SQSTM1, and p62/SQSTM1 can interact with RIPK1.
A: The expression levels of p62/SQSTM1 and LC3II were evaluated in HT29 and HCT116 cells after exposure to OSW-1 for 24 h; B: The gene expression levels of p62/SQSTM1 and LC3 were assessed in HT29 and HCT116 cells after 24 h of exposure to OSW-1; C: Representative images of HT29 cells and HCT116 cells infected with adenovirus expressing GFP-mCherry-LC3. Cells not treated with OSW-1 served as the control. The images show total autophagosomes (yellow puncta) and functional autophagolysosomes (red puncta); D: Coimmunoprecipitation was conducted to assess the interaction between RIPK1 and p62/SQSTM1, and the results were analyzed through western blotting; E: Representative confocal microscopy images showing the colocalization of p62/SQSTM1 and RIPK1 in HT29 and HCT116 cells after exposure to OSW-1 for 24 h, with or without the addition of necrostatin-1. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs Control. Each data point represents the mean ± SE. PI: Propidium iodide; Nec-1: Necrostatin-1.
- Citation: Wang N, Li CY, Yao TF, Kang XD, Guo HS. OSW-1 triggers necroptosis in colorectal cancer cells through the RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL signaling pathway facilitated by the RIPK1-p62/SQSTM1 complex. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(15): 2155-2174
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i15/2155.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i15.2155