Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2024; 30(15): 2155-2174
Published online Apr 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i15.2155
Published online Apr 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i15.2155
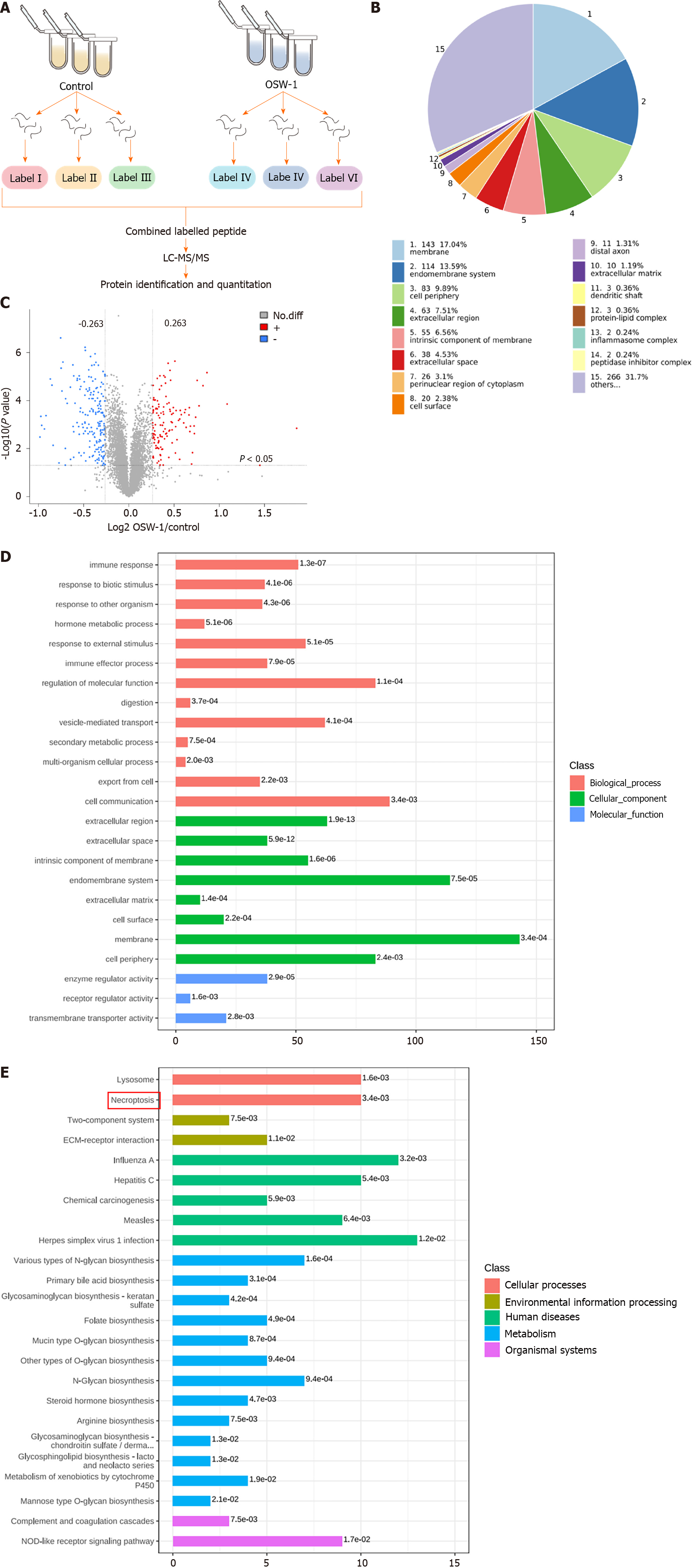
Figure 2 Quantitative proteomic analysis was also conducted on control and OSW-1-treated colorectal cancer cells, and bioinformatic analyses were subsequently performed on the differentially expressed proteins.
A: Schematic diagram outlining the process of proteomic analysis in this study; B: Subcellular localization of proteins that were altered by OSW-1; C: Volcano plot showing OSW-1-induced changes in proteins; red dots indicate increased proteins, and blue dots indicate decreased proteins; D: The top 20 enriched gene ontology (GO) terms were identified using Fisher’s exact test for the biological process, molecular function, and cellular component categories. The vertical axis shows the GO terms in each category, while the horizontal axis shows the protein number for each item. The numbers beside the bars indicate enrichment factors, indicating the significance and reliability of the proteins enriched in each item; E: Enriched Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways associated with the differentially expressed proteins, with the numbers beside the bars representing the P value calculated using Fisher’s exact test.
- Citation: Wang N, Li CY, Yao TF, Kang XD, Guo HS. OSW-1 triggers necroptosis in colorectal cancer cells through the RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL signaling pathway facilitated by the RIPK1-p62/SQSTM1 complex. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(15): 2155-2174
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i15/2155.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i15.2155