Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2024; 30(14): 2038-2058
Published online Apr 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.2038
Published online Apr 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.2038
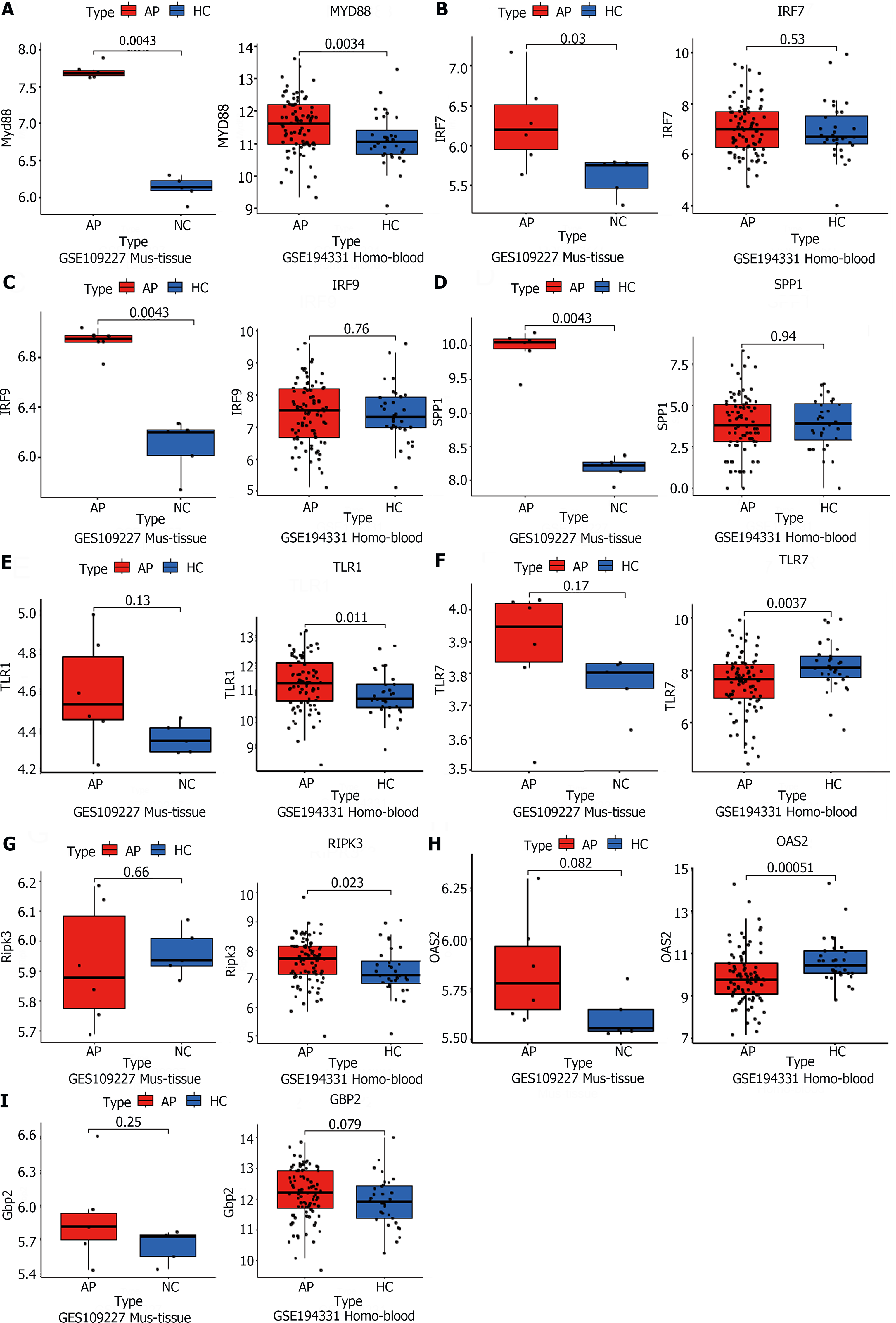
Figure 4 Public RNA-seq data reveals that the significant role of TLR and NOD-like signaling pathways in acute pancreatitis pathogenesis.
A-I: The acute pancreatitis (AP) animal RNA-seq dataset (GSE109227) and human AP patient blood RNA-seq dataset (GSE194331) were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database for the external validation of significant differentially expressed genes in the successfully validated NOD-like receptor and TLR signaling pathways in the animal model, using quantitative real-time PCR. n = 6 per group.
- Citation: Zheng P, Li XY, Yang XY, Wang H, Ding L, He C, Wan JH, Ke HJ, Lu NH, Li NS, Zhu Y. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals the molecular changes of acute pancreatitis in experimental models. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(14): 2038-2058
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i14/2038.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.2038