Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2024; 30(14): 2018-2037
Published online Apr 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.2018
Published online Apr 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.2018
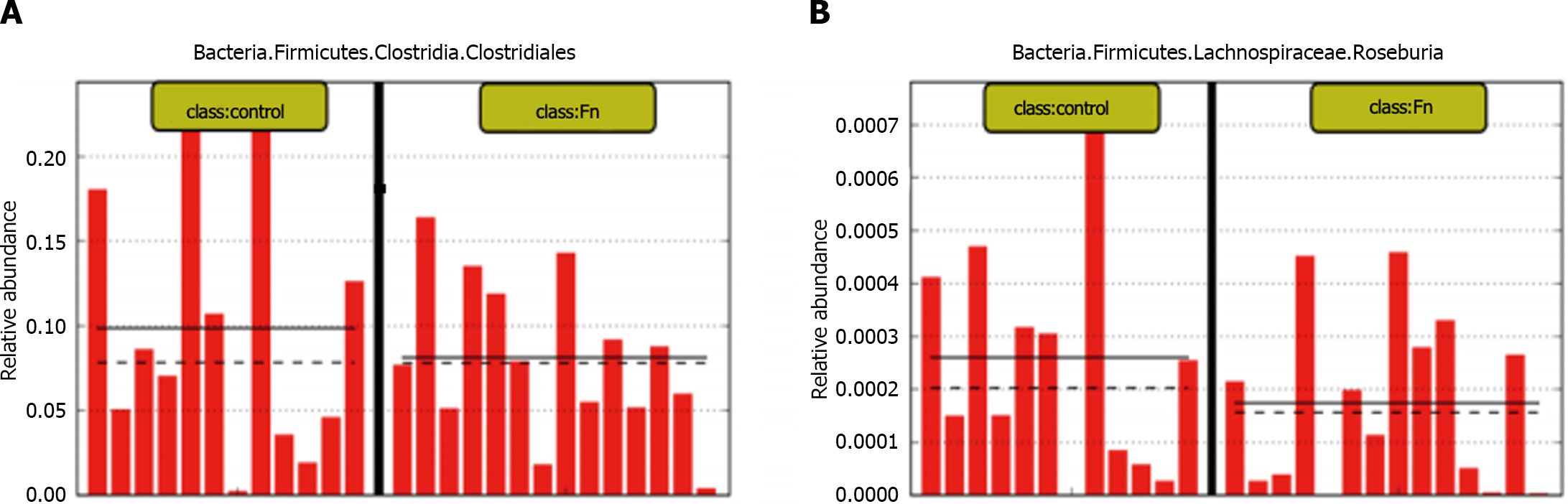
Figure 3 Abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria is decreased in mice treated with Fusobacteriumnucleatum.
A and B: The 16S rDNA sequencing results showed that the abundance of fecal butyric acid-producing bacteria (Lac_Rosebaria and Clostridium) was lower than those of the control group in mice treated with Fusobacterium nucleatum by gavage (n = 12 for each group). Each bar represents the content of Clostridium (A) or Lactobacillus (B) in the feces of mice in the treatment group.
- Citation: Wu QL, Fang XT, Wan XX, Ding QY, Zhang YJ, Ji L, Lou YL, Li X. Fusobacterium nucleatum-induced imbalance in microbiome-derived butyric acid levels promotes the occurrence and development of colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(14): 2018-2037
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i14/2018.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.2018