Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2024; 30(11): 1572-1587
Published online Mar 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1572
Published online Mar 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1572
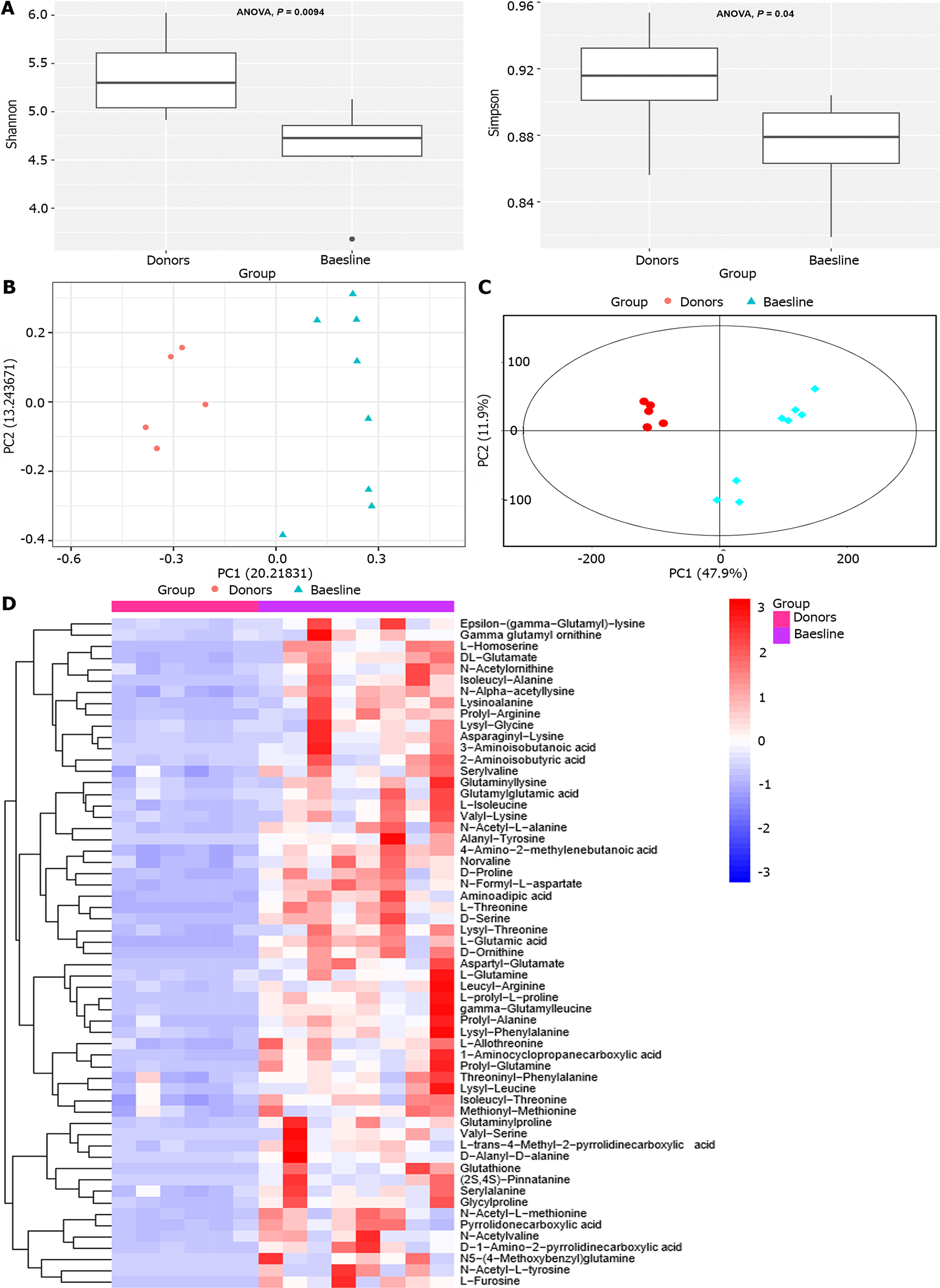
Figure 1 Mildly active Crohn’s disease patients differed from the donors in alpha and beta diversity and metabolites.
A: Baseline Crohn’s disease (CD) patients exhibited significantly lower gut microbiome Shannon’s and Simpson’s index than the donors; B: Comparison of beta diversity of the microbial communities between baseline CD patients and donors. The Jaccard distances from principal coordinate analyses of abundance are depicted as donors (red) and baseline CD patients (blue). The donors’ samples were more tightly clustered than the baseline samples; C: The PCA score plot clearly discriminated between donors (red) and baseline CD patients (blue), where donors’ samples were more tightly clustered than baseline CD patients’ samples; D: The heat map depicts the intensity of amino acid in the feces of CD patients and donors.
- Citation: Chen SJ, Zhang DY, Wu X, Zhang FM, Cui BT, Huang YH, Zhang ZL, Wang R, Bai FH. Washed microbiota transplantation for Crohn’s disease: A metagenomic, metatranscriptomic, and metabolomic-based study. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(11): 1572-1587
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i11/1572.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1572