Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2024; 30(11): 1480-1487
Published online Mar 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1480
Published online Mar 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1480
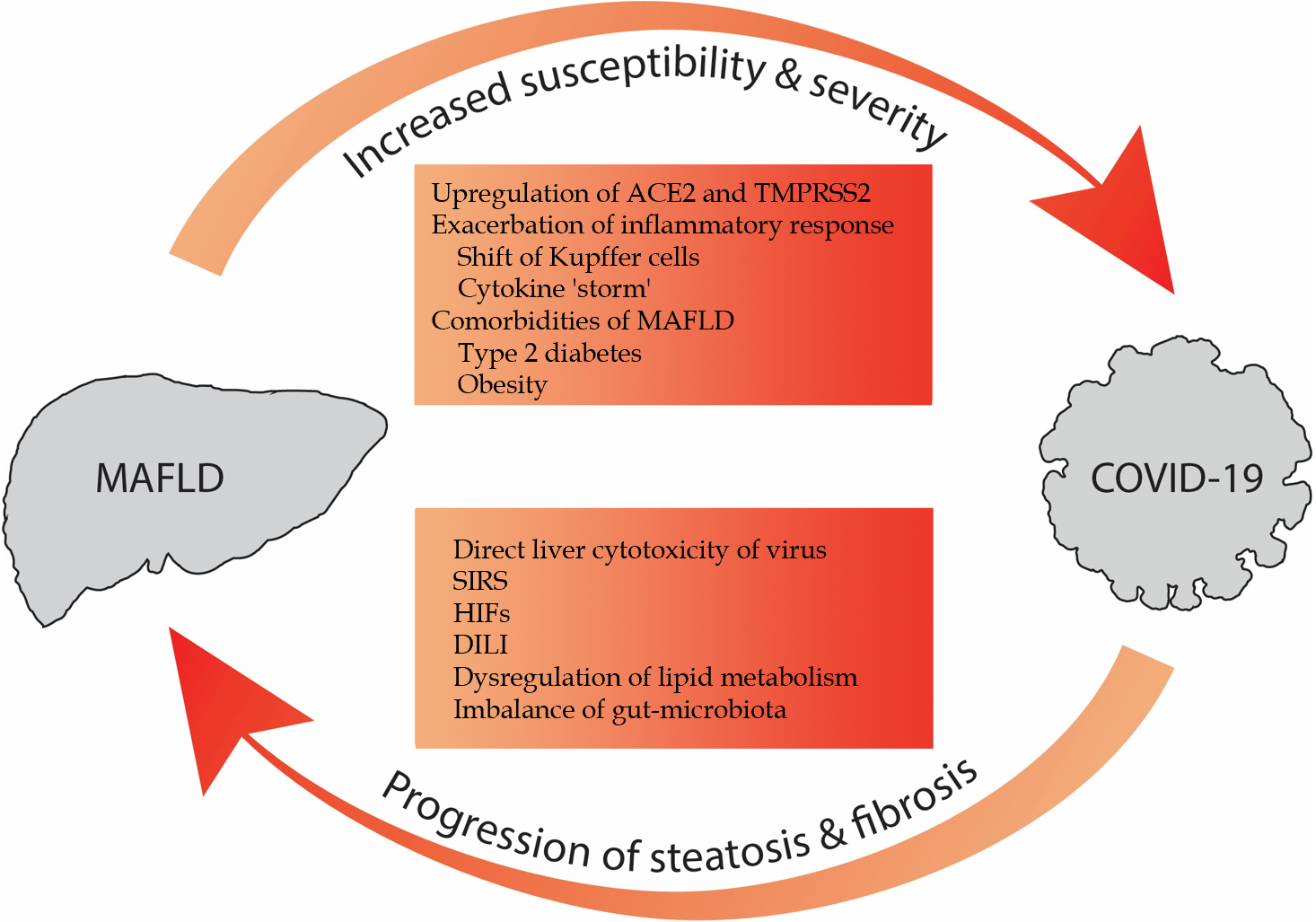
Figure 1 Interplay between coronavirus disease 2019 and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease.
Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) can increase the susceptibility and severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Conversely, COVID-19 can promote the progression of preexisting MAFLD. MAFLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; TMPRSS2: Trans-membrane protease serine 2; SIRS: Systematic inflammatory response syndrome; HIFs: Hypoxia-induced factors; DILI: Drug-induced liver injury; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019.
- Citation: Brilakis L, Theofilogiannakou E, Lykoudis PM. Current remarks and future directions on the interactions between metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and COVID-19. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(11): 1480-1487
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i11/1480.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1480