Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2024; 30(10): 1431-1449
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1431
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1431
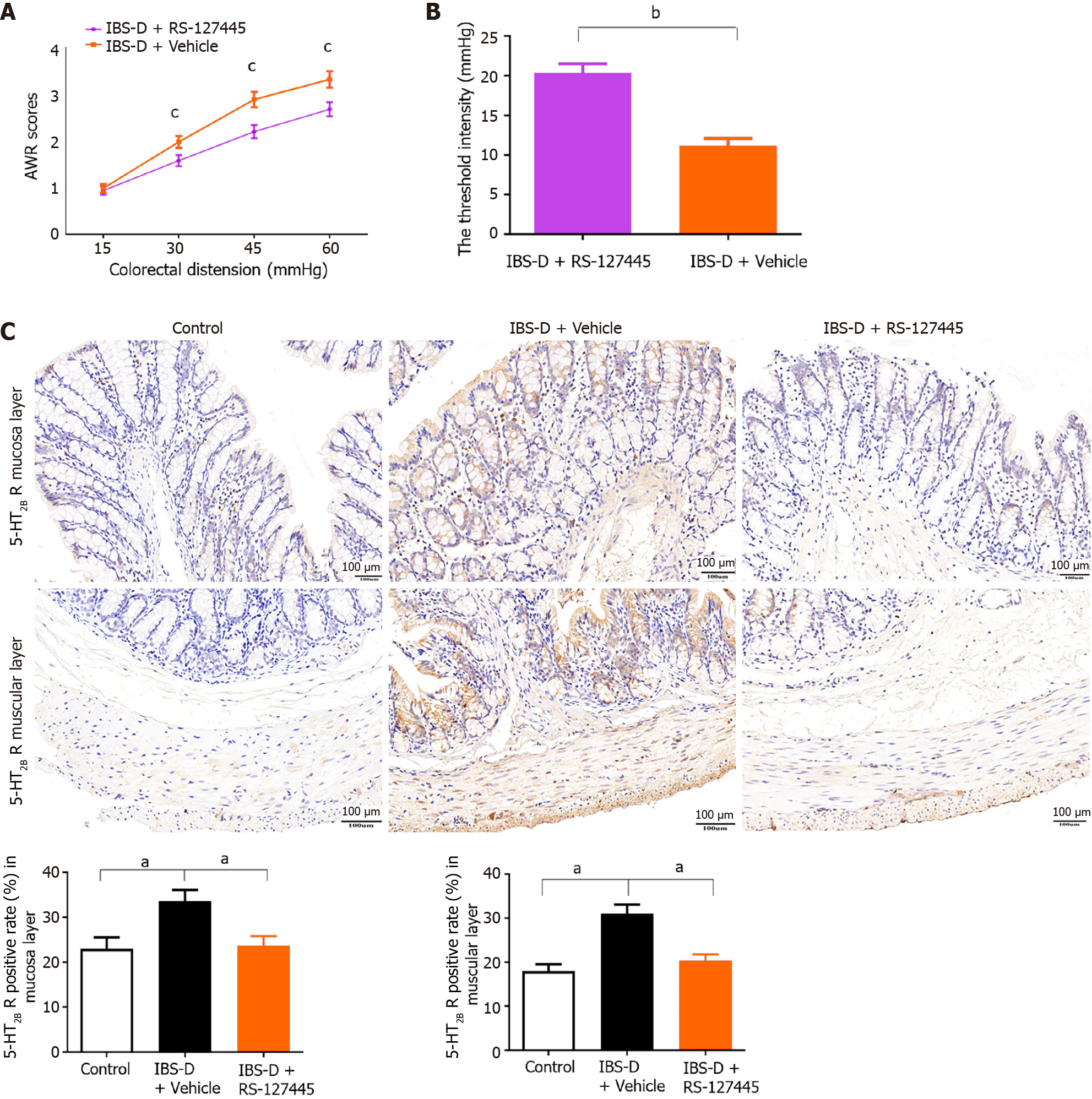
Figure 4 RS12-7445 decreased the visceral sensitivity and serotonin receptor 2B levels in irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea rats.
A: The irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) + Vehicle group had significantly greater abdominal withdrawal reflex scores than did the IBS-D + RS-127445 group with the same colorectal distension (CRD) pressure; B: The IBS-D + Vehicle group had significantly reduced threshold pressure than did the IBS-D + RS-127445 group with the same CRD pressure; C: Immunohistochemical staining showing the expression of the serotonin receptor 2B receptor in the colon mucosa layer and colon muscular layer of each group. Magnification 20 ×; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. IBS-D: Irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea; 5-HT2B: Serotonin receptor 2B; AWR: Abdominal withdrawal reflex.
- Citation: Li ZY, Mao YQ, Hua Q, Sun YH, Wang HY, Ye XG, Hu JX, Wang YJ, Jiang M. Serotonin receptor 2B induces visceral hyperalgesia in rat model and patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(10): 1431-1449
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i10/1431.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1431