Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2024; 30(10): 1405-1419
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1405
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1405
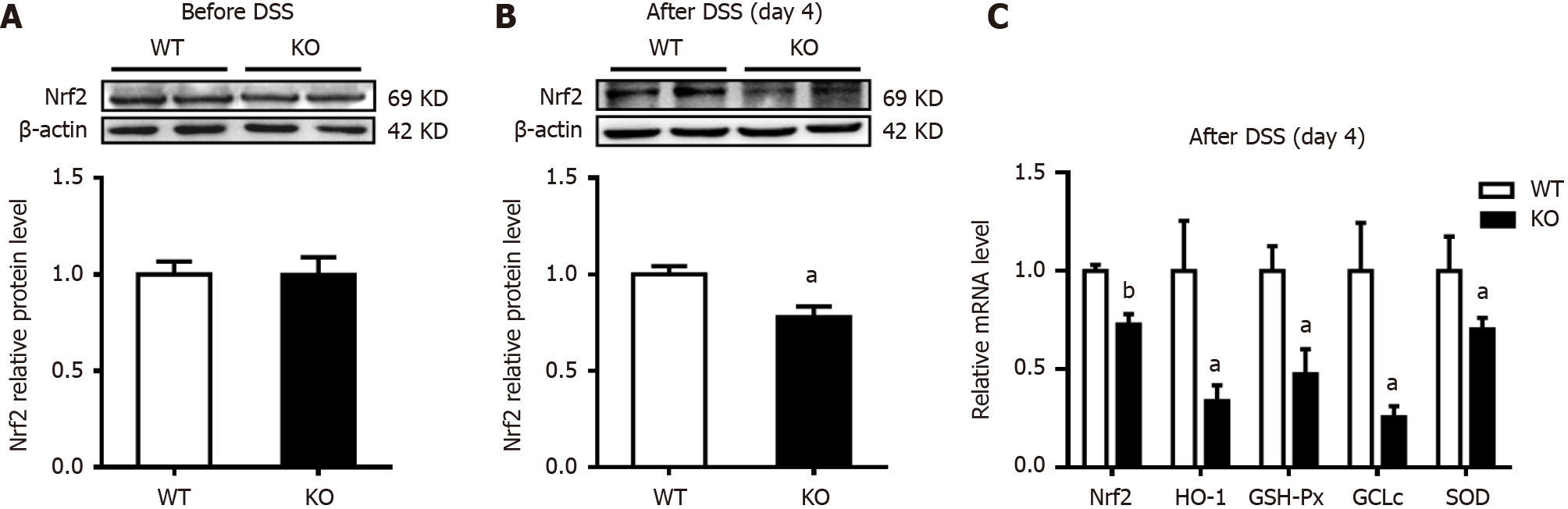
Figure 6 Changes in the expression of colonic nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and antioxidant enzymes after dextran sulfate sodium induction.
The mice were given normal drinking water before dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) treatment, and the mice were then given 3% DSS water for 4 d. A and B: Western blot analysis of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) was performed on homogenates of colonic mucosa tissues before and after DSS induction; C: Quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was used to measure the mRNA levels of Nrf2 and its target antioxidant genes in colonic mucosa tissues. n = 4 per group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 compared with wild-type (WT) mice. GCLc: Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GSH-Px: Glutathione peroxidase; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; KO: Gene knockout; SOD: Superoxide.
- Citation: Tian Y, Li X, Wang X, Pei ST, Pan HX, Cheng YQ, Li YC, Cao WT, Petersen JDD, Zhang P. Alkaline sphingomyelinase deficiency impairs intestinal mucosal barrier integrity and reduces antioxidant capacity in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(10): 1405-1419
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i10/1405.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1405