Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2024; 30(10): 1405-1419
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1405
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1405
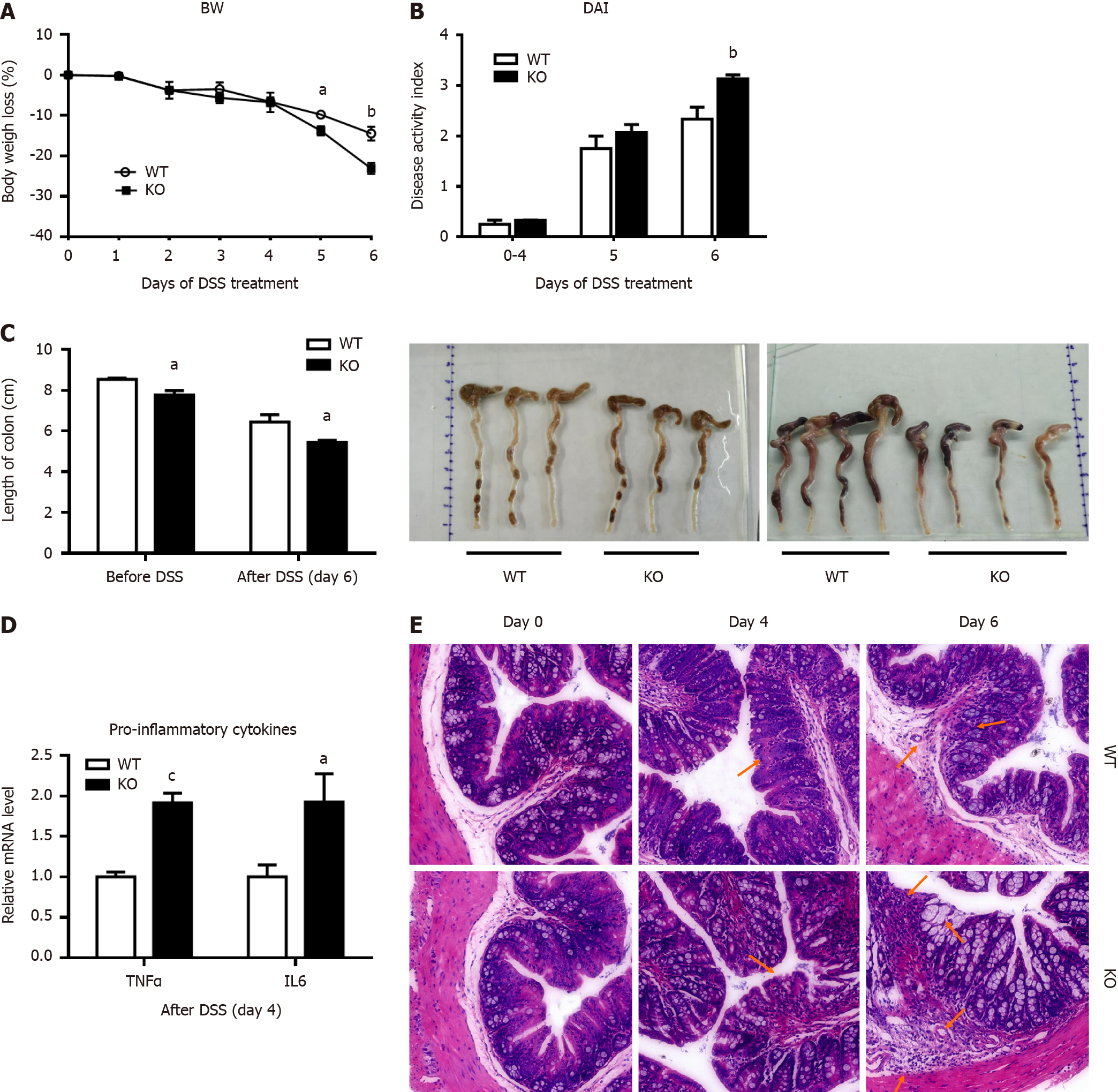
Figure 1 Alkaline sphingomyelinase deficiency exacerbates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice.
The mice were treated with 3% dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) in drinking water for 6 d. A: Body weight (BW) was measured, and the percentage of BW loss was calculated (n = 6 per group); B: The disease activity index (DAI) was calculated according to the stool bleeding score, BW loss, stool consistency, and disease signs (n = 4 per group); C: After 6 d of DSS treatment, the colon was removed, and the length of the colon was measured (before DSS, n = 3 per group; after DSS, n = 4 per group); D: The mRNA levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and interleukin (IL)-6 in colonic mucosal tissue were analyzed (n = 4 per group); E: Histopathological characterization of the colon was performed. Arrows: Decreased goblet cells; dysplastic glands; dilated congested blood vessels; destroyed mucosal layer; severe damage to the intestinal epithelium; intensive inflammatory cell infiltration to the submucosa and muscularis. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.005 compared with wild-type (WT). KO: Gene knockout.
- Citation: Tian Y, Li X, Wang X, Pei ST, Pan HX, Cheng YQ, Li YC, Cao WT, Petersen JDD, Zhang P. Alkaline sphingomyelinase deficiency impairs intestinal mucosal barrier integrity and reduces antioxidant capacity in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(10): 1405-1419
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i10/1405.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1405