Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2024; 30(10): 1346-1357
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1346
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1346
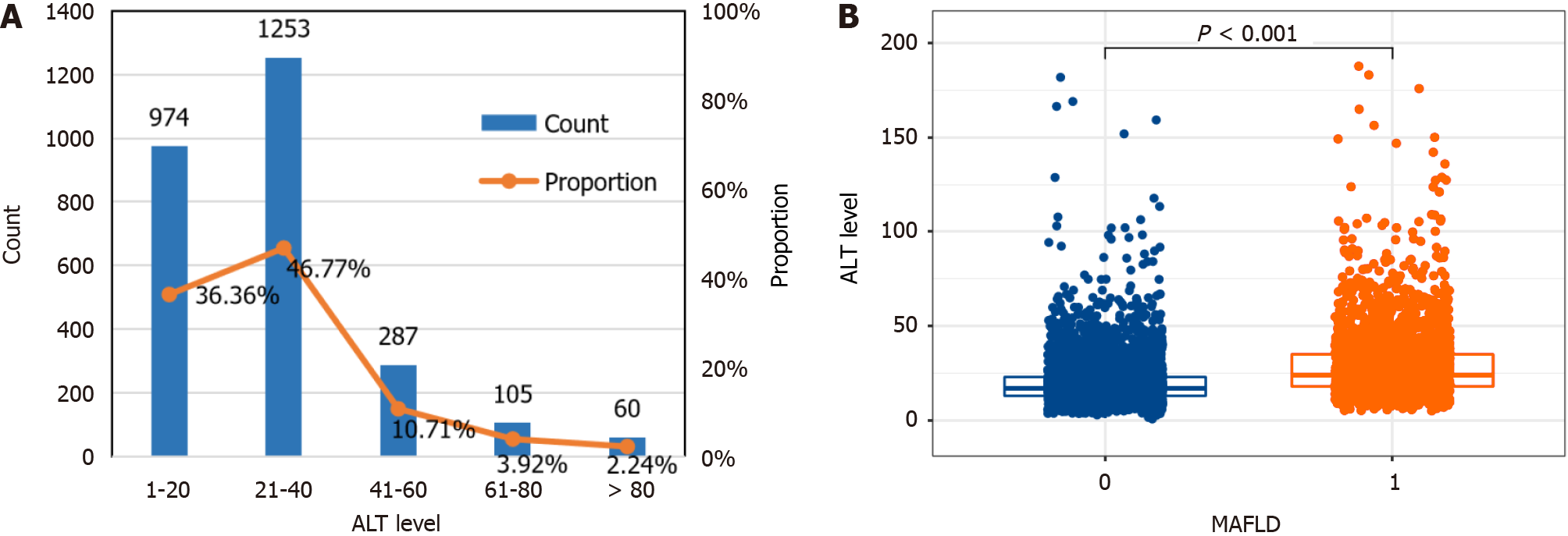
Figure 2 The prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in a large-scale, longitudinal population-based cohort.
A: Distribution of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels in participants with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD); B: Differential analysis of ALT levels between healthy participants and those with MAFLD. The prevalence of MAFLD was 34.27%, and 83.13% of participants with MAFLD had normal ALT levels. ALT levels were significantly greater in MAFLD patients than in healthy individuals. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; MAFLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease.
- Citation: Chen JF, Wu ZQ, Liu HS, Yan S, Wang YX, Xing M, Song XQ, Ding SY. Cumulative effects of excess high-normal alanine aminotransferase levels in relation to new-onset metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in China. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(10): 1346-1357
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i10/1346.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1346