Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2024; 30(10): 1346-1357
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1346
Published online Mar 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1346
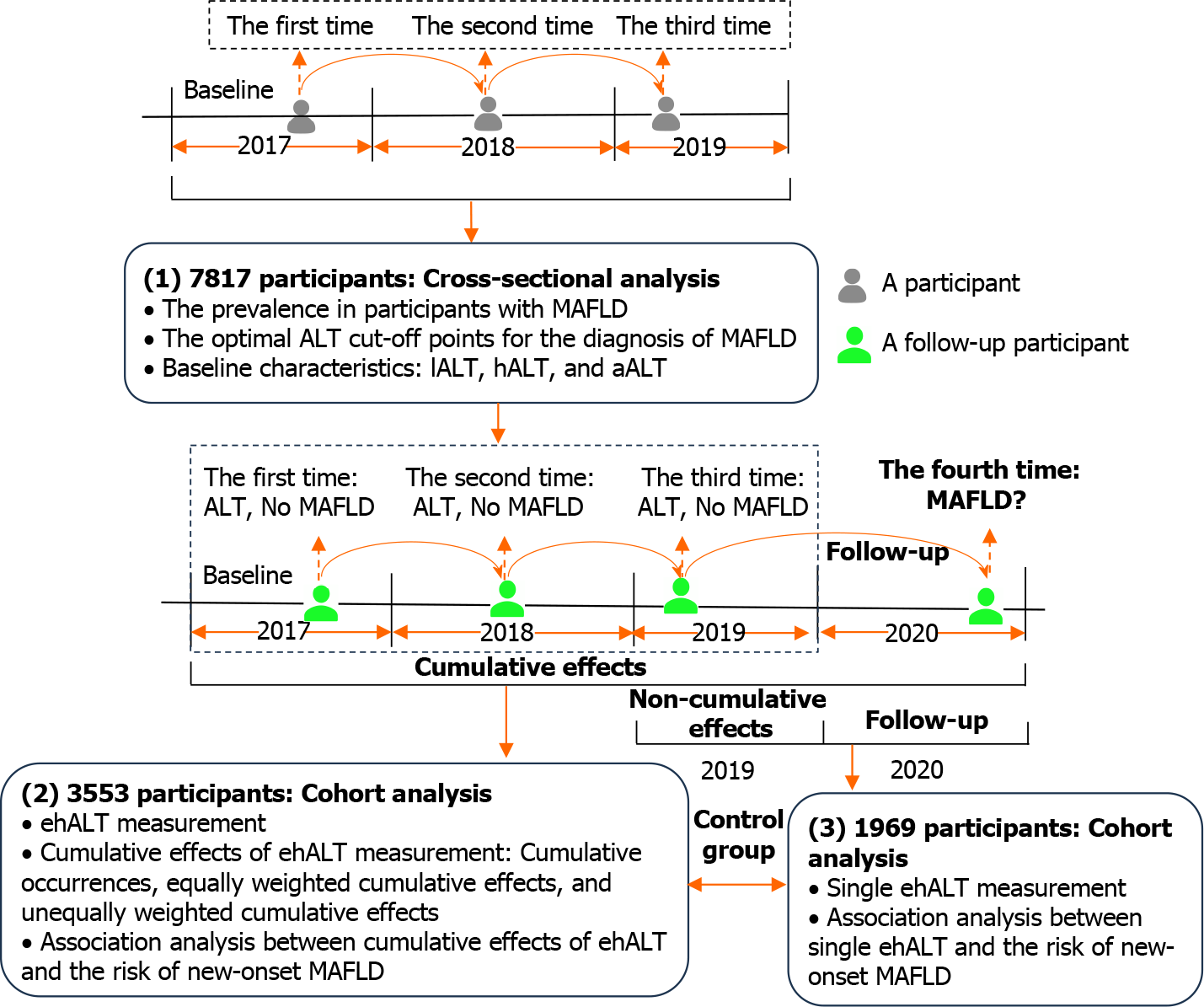
Figure 1 Schematic description of the study design.
7817 participants with three consecutive health examinations from 2017 to 2019 were analysed to determine the optimal alanine aminotransferase (ALT) cut-off points for the diagnosis of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). A follow-up cohort of 3553 participants who completed their fourth health examination in 2020 was subsequently analysed to calculate the cumulative effects of excess high-normal ALT and explore its association with the risk of new-onset MAFLD. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; MAFLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; lALT: Low-normal alanine aminotransferase; hALT: High-normal alanine aminotransferase; aALT: Abnormal alanine aminotransferase; ehALT: Excess high-normal alanine aminotransferase.
- Citation: Chen JF, Wu ZQ, Liu HS, Yan S, Wang YX, Xing M, Song XQ, Ding SY. Cumulative effects of excess high-normal alanine aminotransferase levels in relation to new-onset metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in China. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(10): 1346-1357
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i10/1346.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i10.1346