Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2023; 29(9): 1446-1459
Published online Mar 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i9.1446
Published online Mar 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i9.1446
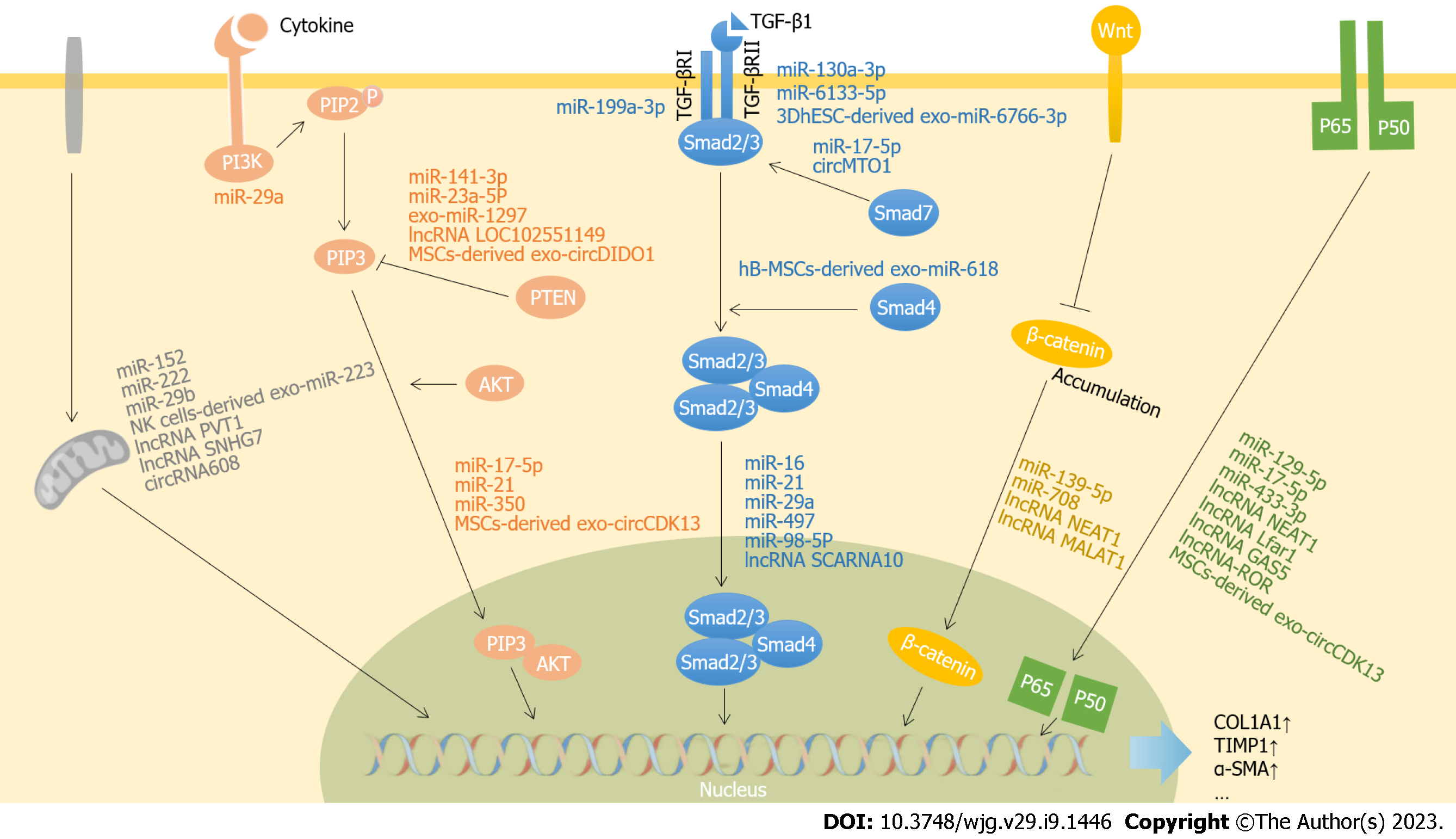
Figure 1 Reported pathways and targets of noncoding RNAs involved in liver fibrosis.
Noncoding RNAs regulate the target gene transcription in the pathogenesis and progression of liver fibrosis through inhibiting or activating the key genes in different signaling pathways. PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: Serine/threonine kinase 1; PIP2: Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biophosphate; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homology deleted on chromosome ten; Col1A1: Collagen 1A1; TIMP1: Targeted tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase1; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin; PIP3: Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; TGF-βRII: TGF-β type II receptor; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; hB-MSC: Human bone MSC; hT-MSC: Human tonsil-derived MSC; 3DhESC: 3D-cultured human embryonic stem cells;PVT1: Plasmacytoma variant translocation 1; SNHG7: Small nucleolar RNA host gene 7; DIDO1: Death inducer-obliterator 1; CDK13: Cyclin dependent kinase 13; MTO1: Mitochondrial tRNA translation optimization 1; SCARNA10: Small Cajal body-specific RNA 10; MALAT1: Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript1; NEAT1: Nuclear enriched abundant transcript1; Lfar1: Liver fibrosis associated lncRNA1; GAS5: Growth arrest-special transcript 5; ROR: Regulator of reprogramming.
- Citation: Li QY, Gong T, Huang YK, Kang L, Warner CA, Xie H, Chen LM, Duan XQ. Role of noncoding RNAs in liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(9): 1446-1459
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i9/1446.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i9.1446