Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2023; 29(6): 1026-1053
Published online Feb 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.1026
Published online Feb 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.1026
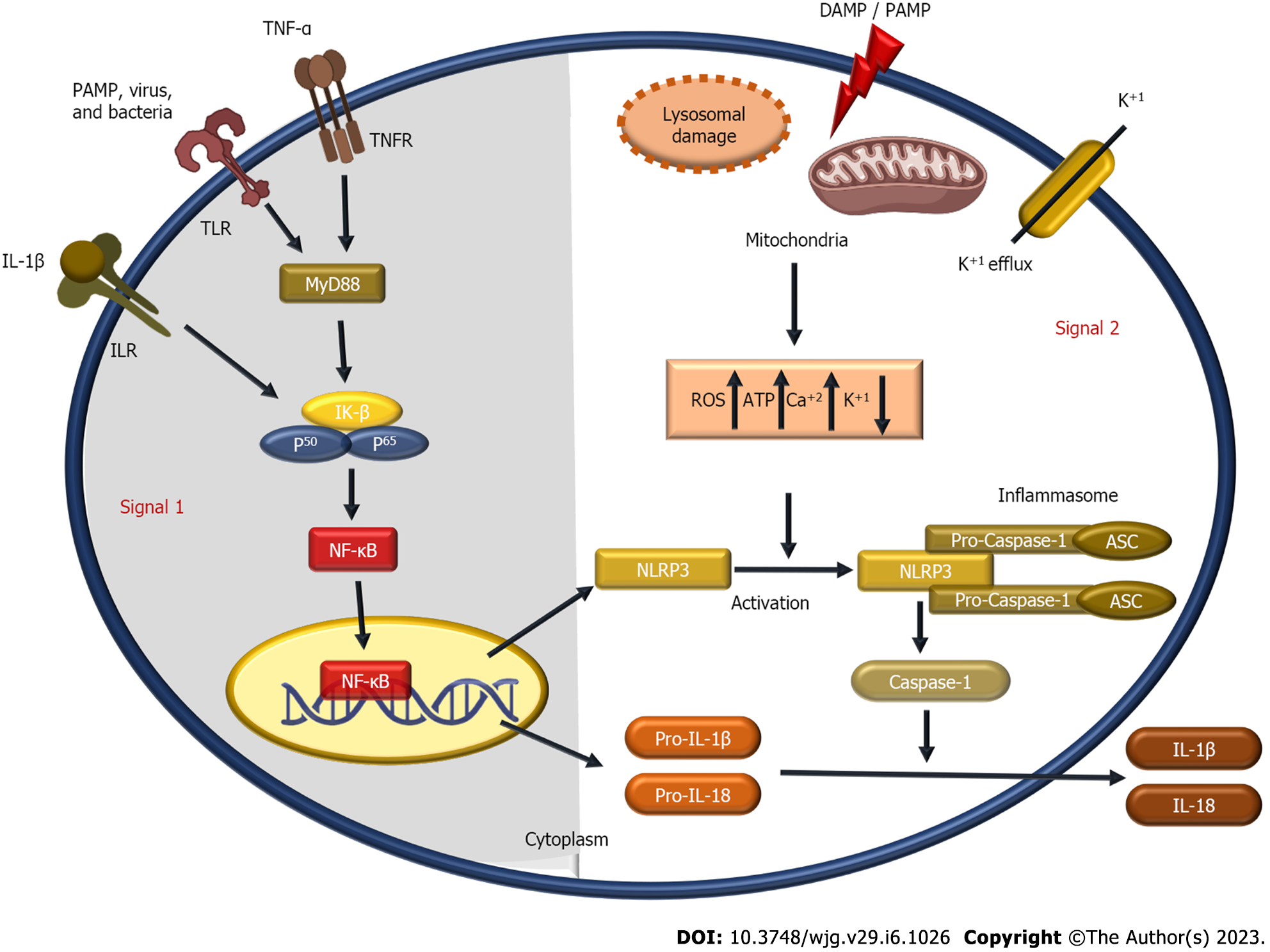
Figure 2 The mechanism of nod-like receptor protein-3 inflammasome activation.
Nod-like receptor protein-3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation occurs through two signals, (signal 1) toll-like receptor stimulation by pathogen associated molecular pattern (PAMP), bacteria and viruses, tumour necrosis factor receptor stimulation by TNF-α, and interleukin receptor (ILR) stimulation by IL-1β leads to activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-Κb) via upregulation of MyD88, and Iκ-β, P50, and P65 complex. Pro-IL-1β, pro-IL-18, and inactive NLRP3 expression were all increased by the translocation of activated NF-κB into the nucleus. (Signal 2) Increased intracellular reactive oxygen species, adenosine triphosphate, and Ca+ levels are caused by damage associated molecular pattern and PAMP-induced lysosomal damage, and mitochondrial dysfunction, while K+ efflux lowered intracellular K+ level. The previous intracellular events lead to activates NLRP3 to inflammasome that promotes caspase-1 which begin to convert pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into IL-1β and IL-18. IL-(1β): Interleukin-1 beta; DAMP: Damage associated molecular pattern; PAMP: Pathogen associated molecular pattern; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor-alpha; ILR: Interleukin receptor; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TNFR: Tumour necrosis factor receptor; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation primary response 88; IK-β: Inhibitor kappa-beta; P50: Nuclear factor-kappa B P50 subunit; P65: Nuclear factor-kappa B P65 subunit; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; Ca+: Calcium ion; K+: Potassium ion; NF-Κb: Nuclear factor-kappa B; NLRP3: Nod-like receptor protein-3; ASC: Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein.
- Citation: Ali FE, Ibrahim IM, Ghogar OM, Abd-alhameed EK, Althagafy HS, Hassanein EH. Therapeutic interventions target the NLRP3 inflammasome in ulcerative colitis: Comprehensive study. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(6): 1026-1053
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i6/1026.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.1026