Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2023; 29(5): 851-866
Published online Feb 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i5.851
Published online Feb 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i5.851
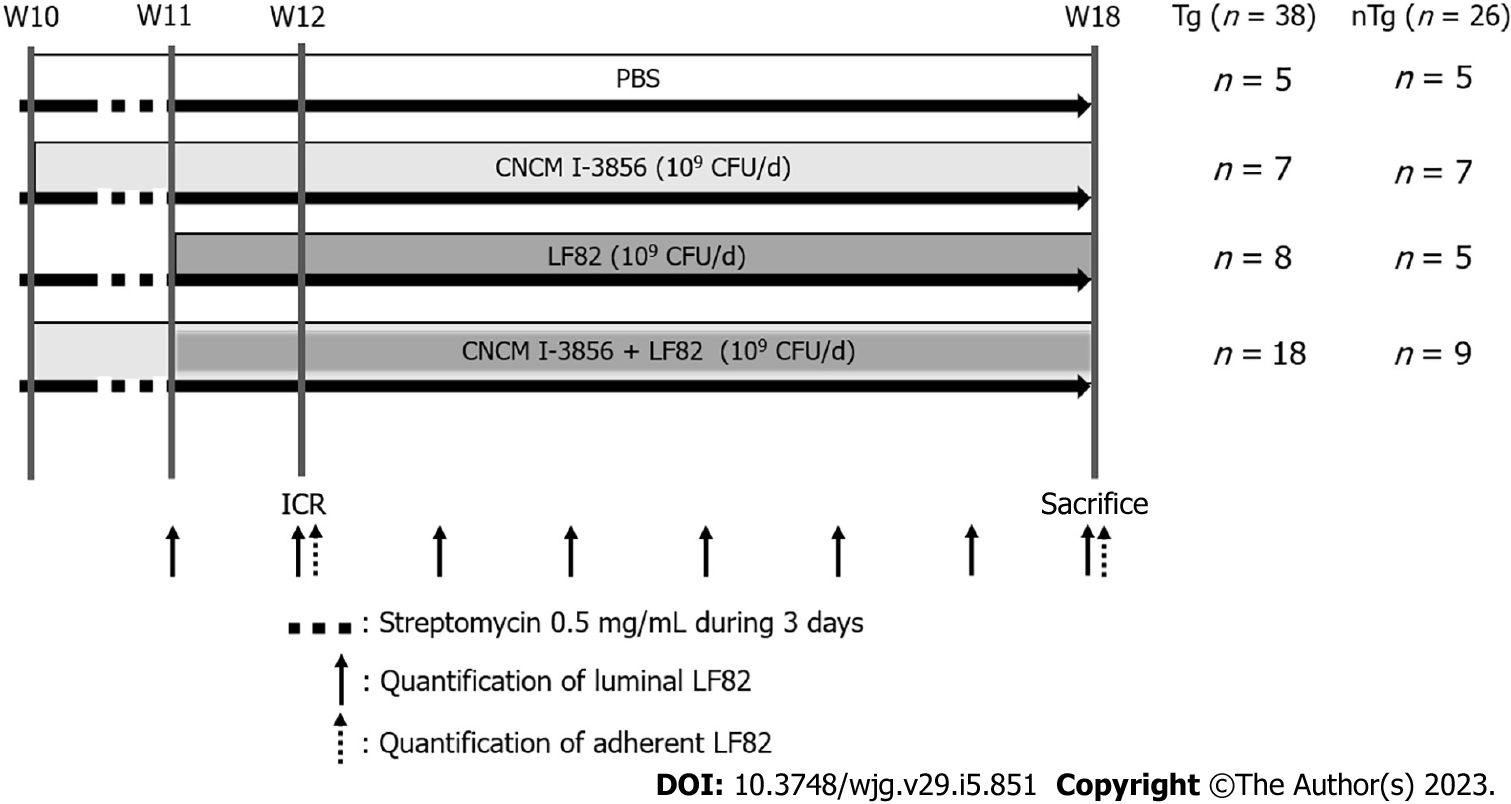
Figure 1 Study design.
HLA-B27 transgenic rats (Tg) and wild-type rats (nTg) were randomized to receive phosphate buffered saline (n = 10), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae) CNCM I-3856 (n = 14), adherent-invasive Escherichia coli strain LF82 (n = 13), or S. cerevisiae CNCM I-3856 and LF82 (n = 27) by oral gavage from week (W) 10 or 11 to W18. Ileocecal resection was performed at W12, and animals were sacrificed at W18. Streptomycin (dotted line) was given on the last 3 d of W10 in all rats. Luminal (arrows) and/or adherent (dotted arrows) LF82 was quantified weekly during the 8-wk study. CFU: Colony-forming unit; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; ICR: Ileocecal resection; d: Day.
- Citation: Valibouze C, Speca S, Dubuquoy C, Mourey F, M'Ba L, Schneider L, Titecat M, Foligné B, Genin M, Neut C, Zerbib P, Desreumaux P. Saccharomyces cerevisiae prevents postoperative recurrence of Crohn's disease modeled by ileocecal resection in HLA-B27 transgenic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(5): 851-866
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i5/851.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i5.851