Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2023; 29(45): 5974-5987
Published online Dec 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i45.5974
Published online Dec 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i45.5974
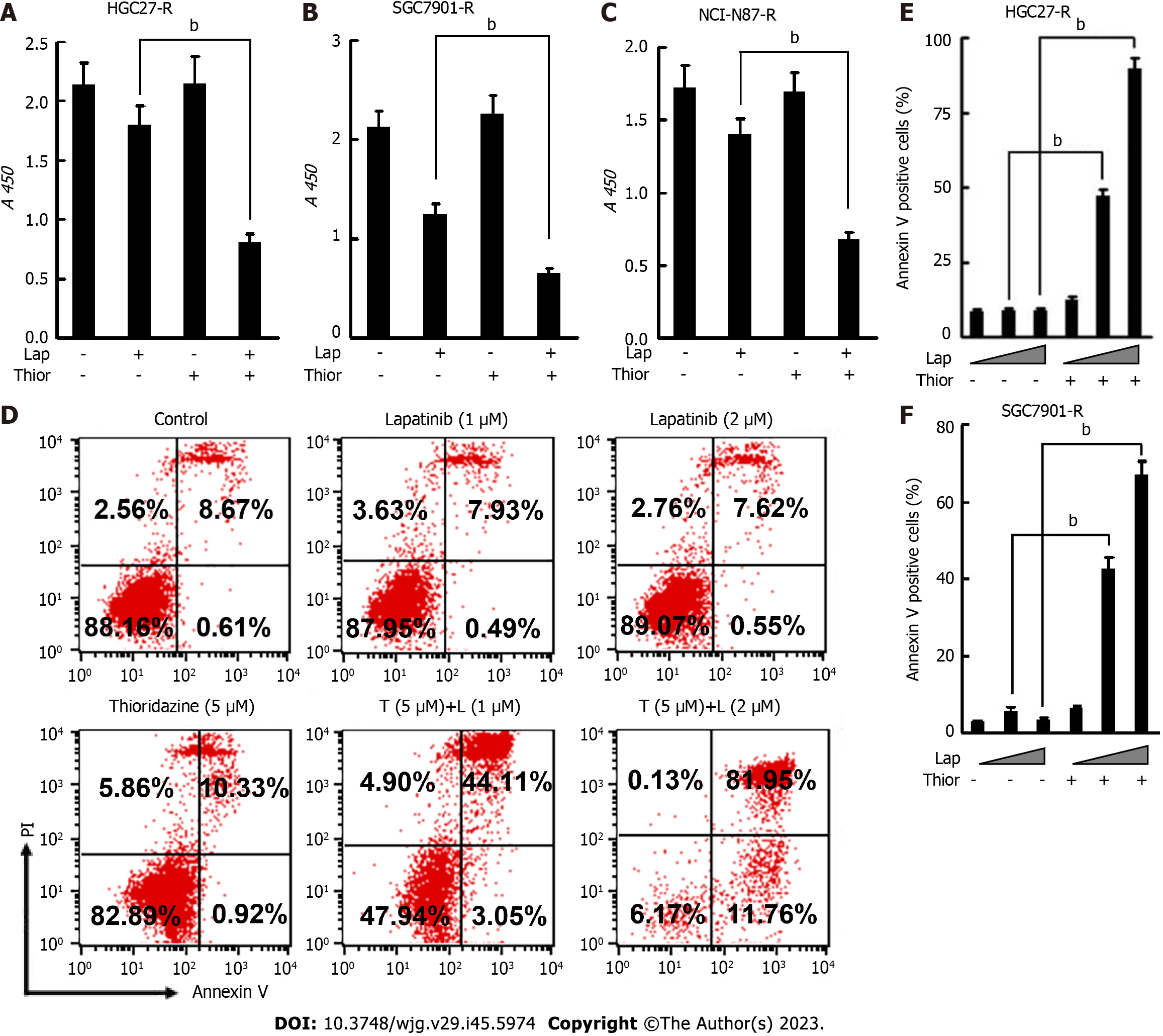
Figure 5 The combination of thioridazine and lapatinib exhibits more pronounced antitumor activity than either alone in vitro against trastuzumab-resistant gastric cancercells.
A-C: To HGC27-R, SGC7901-R, and NCI-N87-R cells were treated with trastuzumab (10 μg/mL) or thioridazine (5 μM) alone or in combination for 48 h. Proliferation activity was evaluated by cell counting kit-8 assays; D-F: HGC27-R cells were treated with lapatinib (1 μM or 2 μM) in the presence or absence of thioridazine (5 μM) for 24 h, followed by an apoptosis assay. Similar experiments were performed and results were quantified in SGC7901-R cells. The experiments were repeated three times. bP < 0.01. Thior: Thioridazine; Lap: Lapatinib.
- Citation: Yang ZY, Zhao YW, Xue JR, Guo R, Zhao Z, Liu HD, Ren ZG, Shi M. Thioridazine reverses trastuzumab resistance in gastric cancer by inhibiting S-phase kinase associated protein 2-mediated aerobic glycolysis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(45): 5974-5987
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i45/5974.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i45.5974