Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2023; 29(45): 5974-5987
Published online Dec 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i45.5974
Published online Dec 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i45.5974
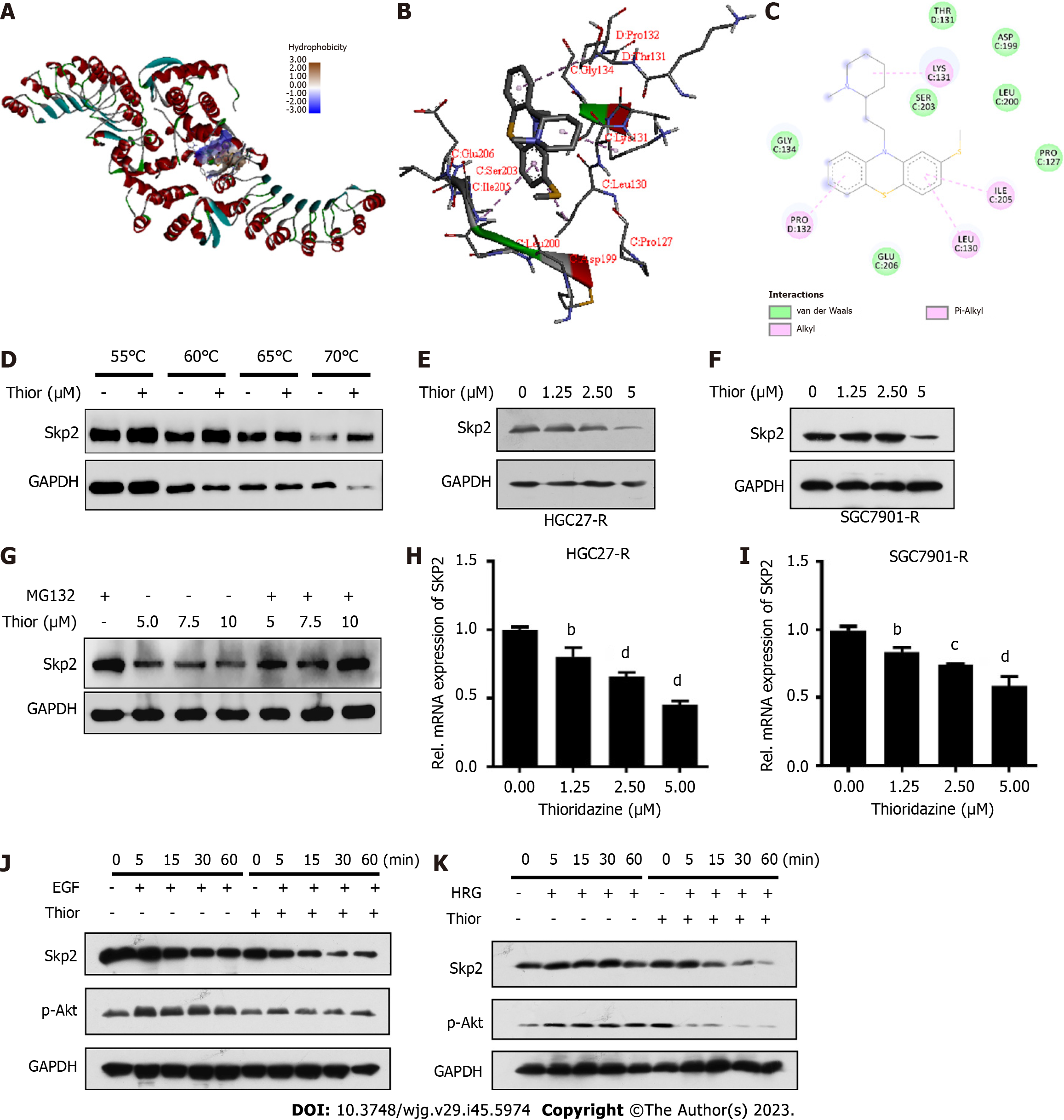
Figure 2 Thioridazine can inhibit S-phase kinase associated protein 2 expression and protein kinase B activation triggered by ErbB signaling.
A: The interaction between the ligand thioridazine and the active pocket of S-phase kinase associated protein 2 (Skp2) (1FS2) was examined; B: 3D structural schematic showing the binding of thioridazine to Skp2; C: Dihedral angle diagram showing the mode of interaction between thioridazine and Skp2; D: HGC-27-R cells were exposed for 24 h to dimethyl sulfoxide or 30 µM thioridazine and subjected to the Cellular Thermal Shift Assay; E and F: HGC27-R and SGC7901-R cells were treated with different concentrations of thioridazine for 24 h. Western blotting was used to analyze Skp2 expression; G: HGC27 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations for 42 h and were then treated with 5 μM MG132 for 6 h. The protein expression level of Skp2 was analyzed by western blotting; H and I: HGC27-R and SGC7901-R cells were treated with various concentrations of thioridazine for 24 h. The mRNA expression level of SKP2 was analyzed by Q-PCR; J and K: HGC27-R cells were pretreated with or without thioridazine (5 μM) for 2 h, followed by stimulation with epidermal growth factor (100 μg/mL) or heregulin (50 μg/mL). At the indicated times, Skp2 and p-protein kinase B protein levels were assessed. bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001; dP < 0.0001. Thior: Thioridazine; Skp2: S-phase kinase associated protein 2; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; HRG: Heregulin.
- Citation: Yang ZY, Zhao YW, Xue JR, Guo R, Zhao Z, Liu HD, Ren ZG, Shi M. Thioridazine reverses trastuzumab resistance in gastric cancer by inhibiting S-phase kinase associated protein 2-mediated aerobic glycolysis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(45): 5974-5987
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i45/5974.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i45.5974