Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2023; 29(44): 5872-5881
Published online Nov 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i44.5872
Published online Nov 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i44.5872
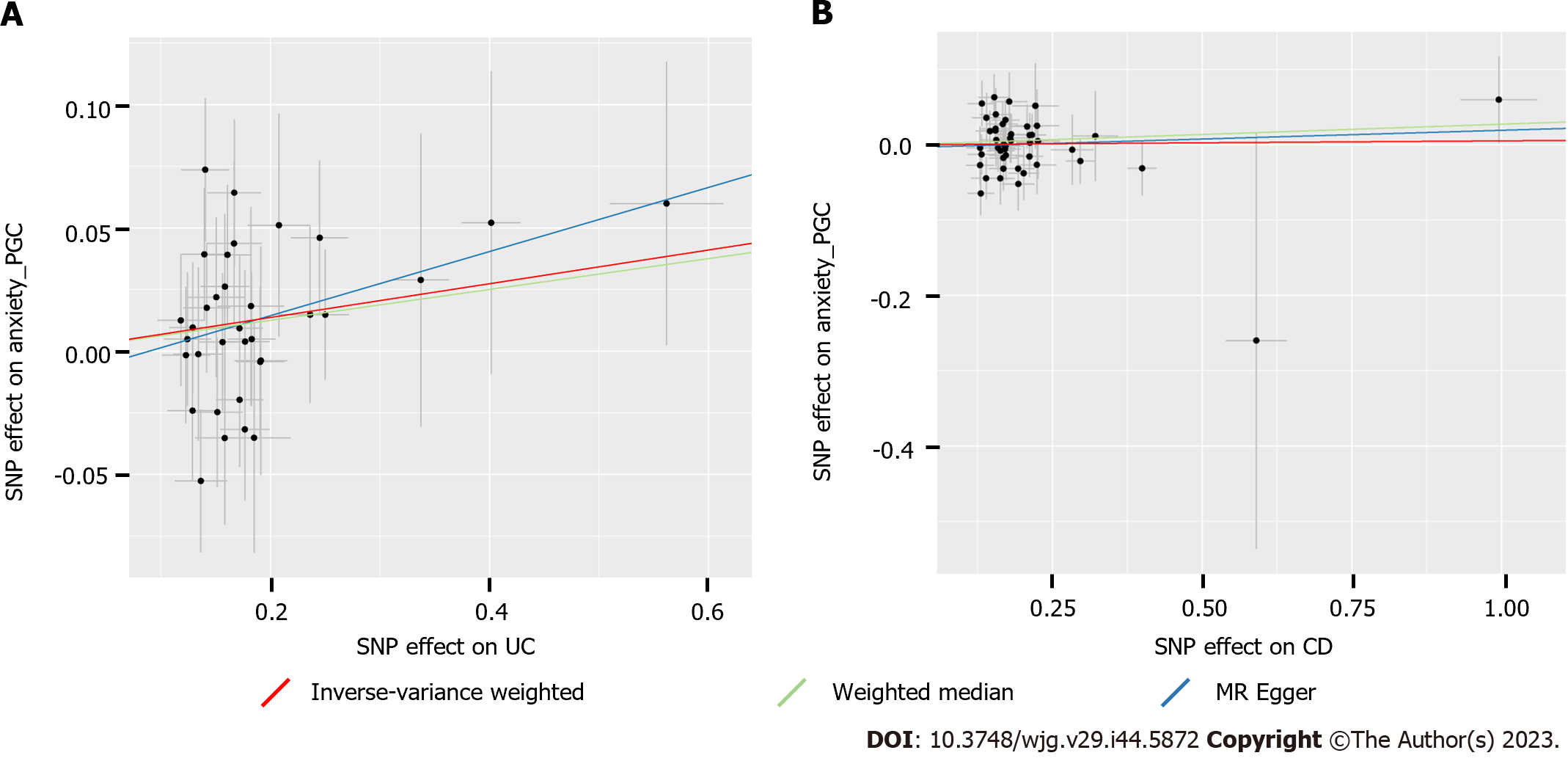
Figure 2 Scatter plots of Mendelian randomization analysis showing the effect of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease on anxiety.
A: Analysis of ulcerative colitis (UC) and anxiety; B: Analysis of Crohn’s disease (CD) and anxiety. The x-axes represent the genetic instrument-UC or instrument-CD associations, and the y-axes represent genetic instrument-anxiety associations. Black dots denote the genetic instruments included in the primary Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis. Red: Inverse-variance weighted; Green: Weighted median; blue: MR Egger. CD: Crohn’s disease; UC: Ulcerative colitis; PGC: Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; SNP: Single-nucleotide polymorphism.
- Citation: He Y, Chen CL, He J, Liu SD. Causal associations between inflammatory bowel disease and anxiety: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(44): 5872-5881
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i44/5872.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i44.5872