Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2023; 29(42): 5699-5715
Published online Nov 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i42.5699
Published online Nov 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i42.5699
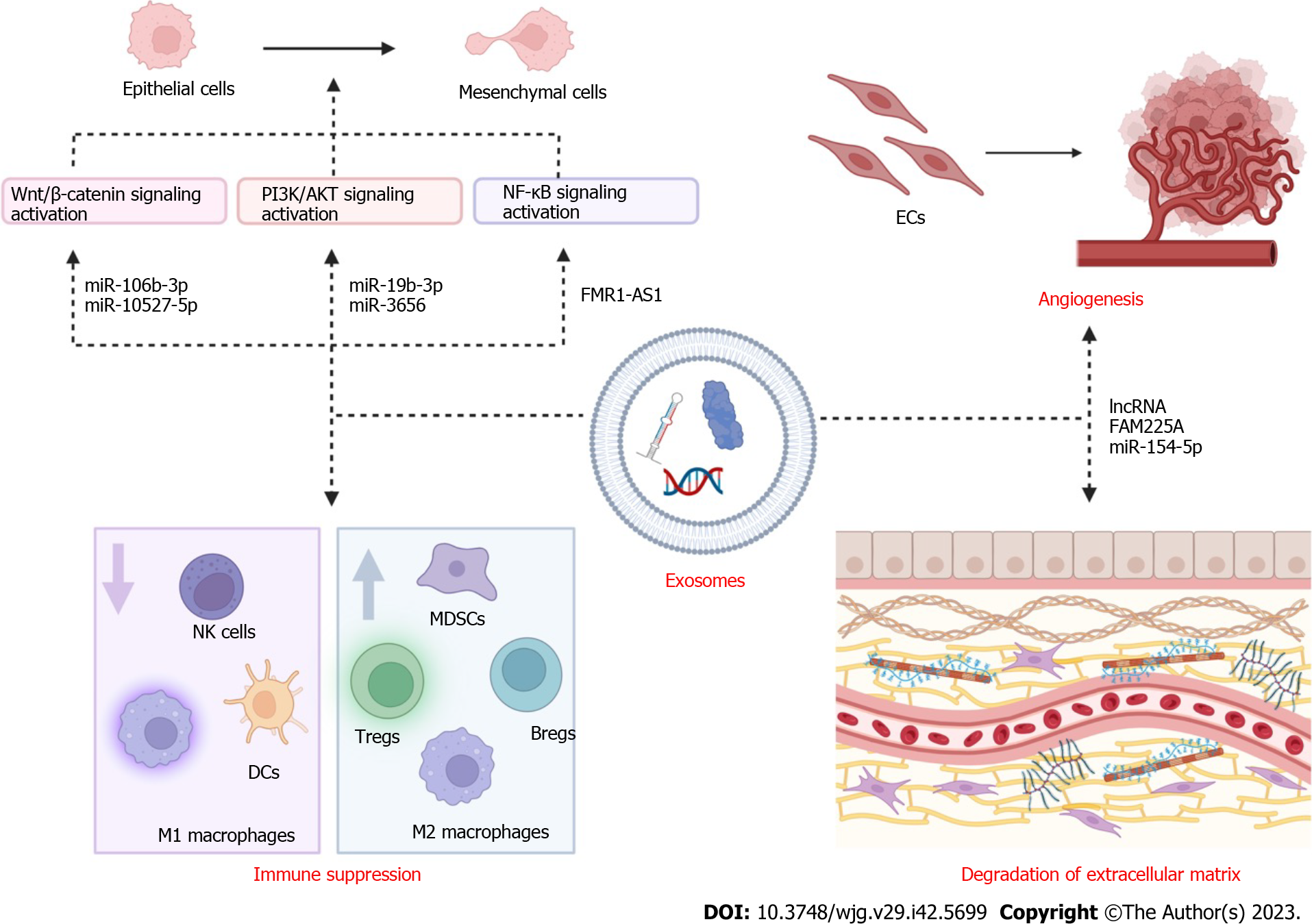
Figure 3 The role of exosomes in esophageal cancer metastasis.
Exosomes are associated with esophageal cancer (EC) metastasis by transferring their contents. The activation of several signaling pathways, including Wnt/β-catenin, PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways, is closely to the exosome-mediated tumor microenvironment in EC. Exosomes can mediate immune suppression by downregulating antitumor cells (including NK cells, dendritic cells and M1 macrophages) and upregulating protumor cells (including myeloid-derived suppressor cells, Tregs, Bregs and M2 macrophages). Additionally, in primary EC sites, degradation of extracellular matrix and angiogenesis are also promoted by exosomes. MDSCs: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; ECs: Esophageal cancers; DCs: Dendritic cells.
- Citation: Ning XY, Ma JH, He W, Ma JT. Role of exosomes in metastasis and therapeutic resistance in esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(42): 5699-5715
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i42/5699.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i42.5699