Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2023; 29(39): 5452-5470
Published online Oct 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452
Published online Oct 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452
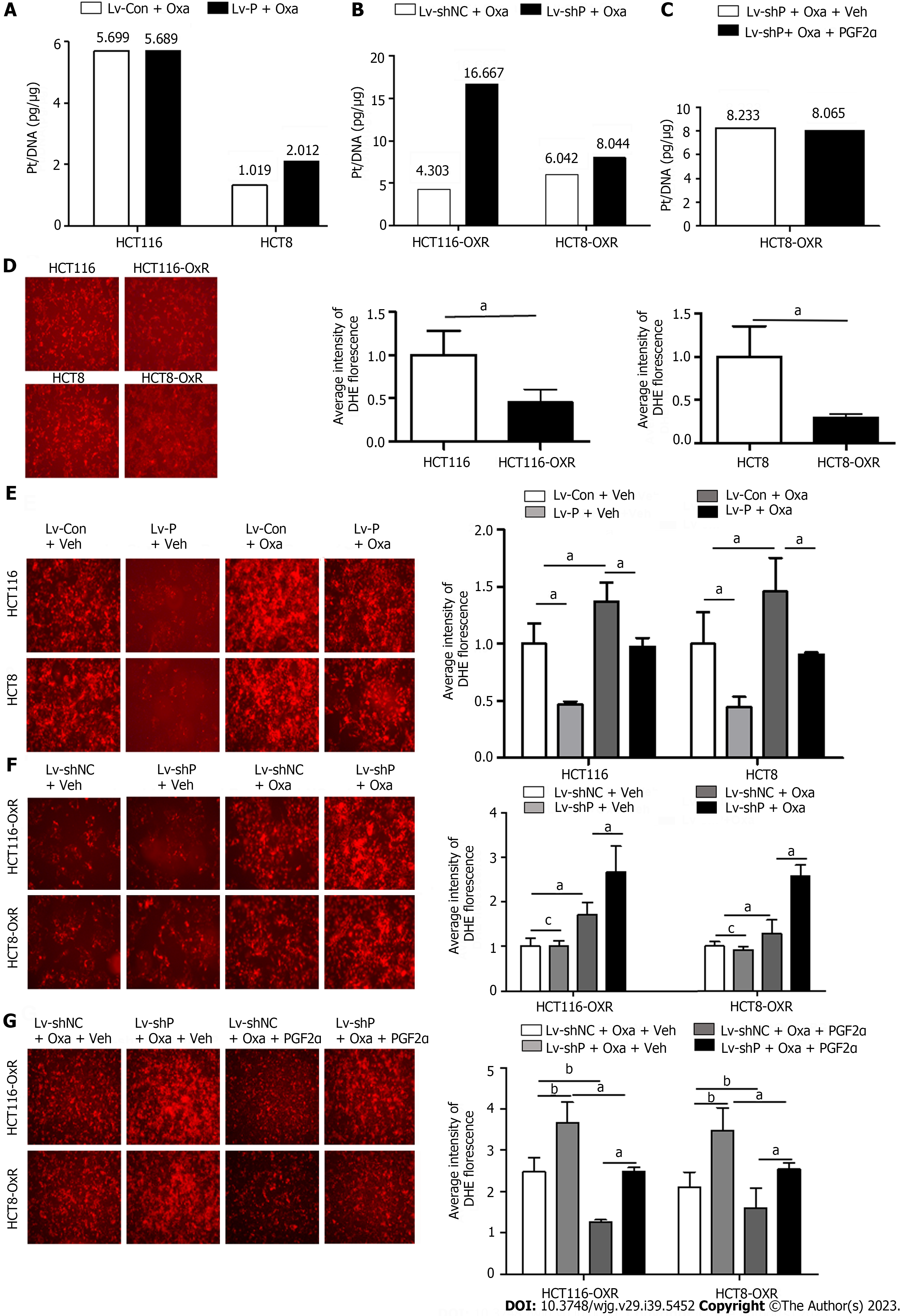
Figure 7 Prostaglandin F2α synthase may suppresses the formation of platinum-DNA adducts.
A: The effect of Prostaglandin F2α synthase (PGF2α) (PGFS) overexpression on the formation of platinum-DNA adducts was determined using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells; B: The effect of PGFS knockdown on the formation of platinum-DNA adducts in oxaliplatin-resistant (OR) CRC cells; C: The effect of PGF2α on the formation of platinum-DNA adducts in OR CRC cells; D: The reactive oxygen species (ROS) content were significantly decreased in OR CRC cells; E: PGFS overexpression significantly decreased ROS content in CRC cells; F: PGFS knockdown significantly decreased ROS content in OR CRC cells; G: PGFS knockdown significantly decreased ROS content in OR CRC cells (scale bar, 50 μm). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01; cNo significance. PGF2α: Prostaglandin F2α; Oxa: Oxaliplatin.
- Citation: Wang YJ, Xie XL, Liu HQ, Tian H, Jiang XY, Zhang JN, Chen SX, Liu T, Wang SL, Zhou X, Jin XX, Liu SM, Jiang HQ. Prostaglandin F2α synthase promotes oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer through prostaglandin F2α-dependent and F2α-independent mechanism. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(39): 5452-5470
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i39/5452.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452