Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2023; 29(39): 5452-5470
Published online Oct 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452
Published online Oct 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452
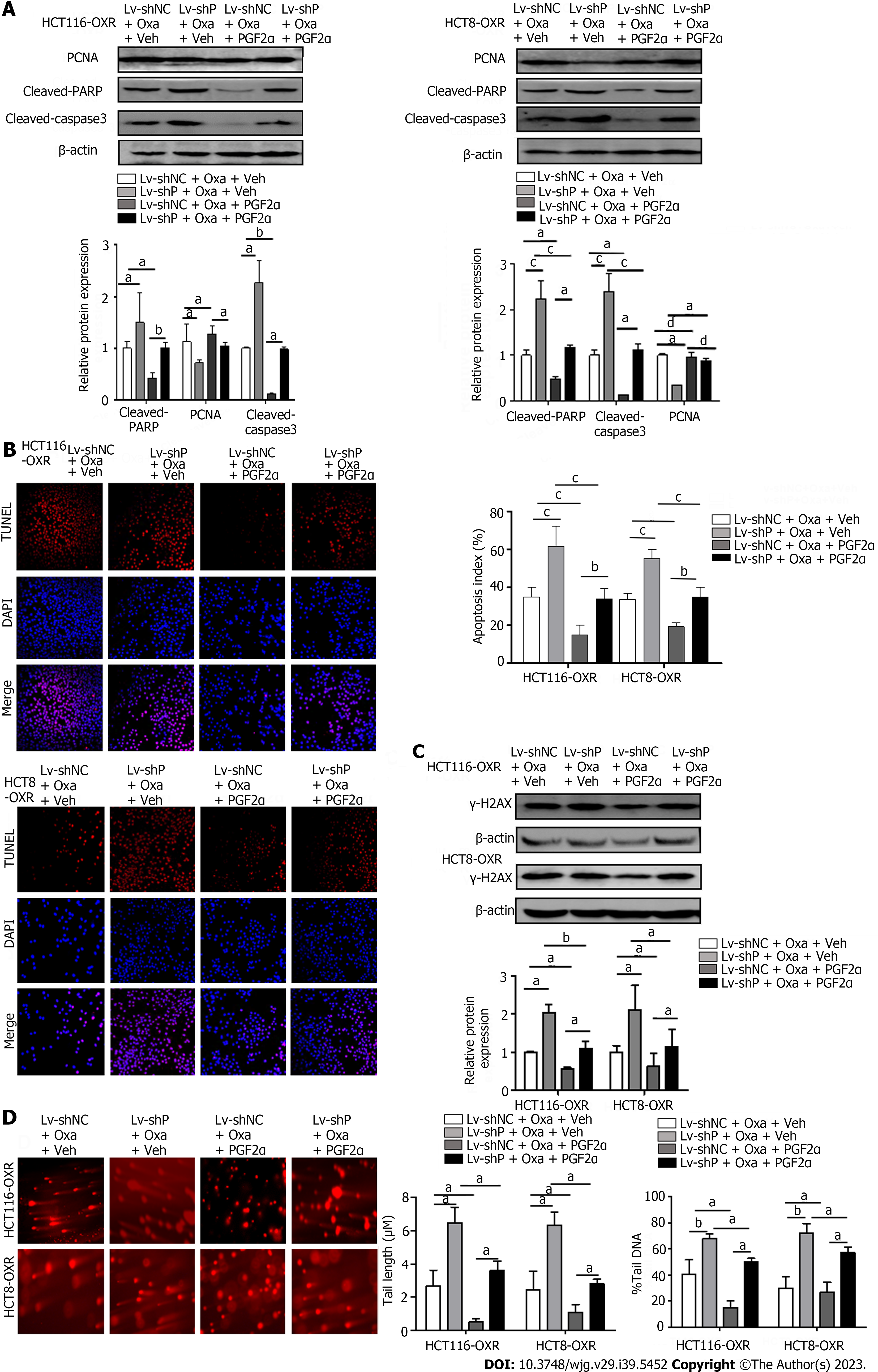
Figure 6 The inhibitory effect of prostaglandin F2α on oxaliplatin-induced cytotoxicity.
A: Western blots showed the effect of prostaglandin F2α synthase (PGF2α) (PGFS) on the expressions of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, cleaved-poly ADP-ribose polymerase, and γ-H2A histone family member X (γ-H2AX) in PGFS knockdown, oxaliplatin-resistant (OR) cells; B: The effect of PGF2α on apoptosis in PGFS knockdown, OR cells evaluated by immunofluorescence. scale bar 100 uM; C: The effect of PGF2α on the cleavage of γ-H2AX protein expressions in PGFS knockdown, OR cells; D: The effect of PGF2α on DNA damage in PGFs knockdown, OR cells evaluated by single-cell gel electrophoresis. scale bar 50 μm). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dNo significance. PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PARP: Poly ADP-ribose polymerase; γ-H2AX: γ-H2A histone family member X; TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling.
- Citation: Wang YJ, Xie XL, Liu HQ, Tian H, Jiang XY, Zhang JN, Chen SX, Liu T, Wang SL, Zhou X, Jin XX, Liu SM, Jiang HQ. Prostaglandin F2α synthase promotes oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer through prostaglandin F2α-dependent and F2α-independent mechanism. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(39): 5452-5470
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i39/5452.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452