Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2023; 29(39): 5452-5470
Published online Oct 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452
Published online Oct 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452
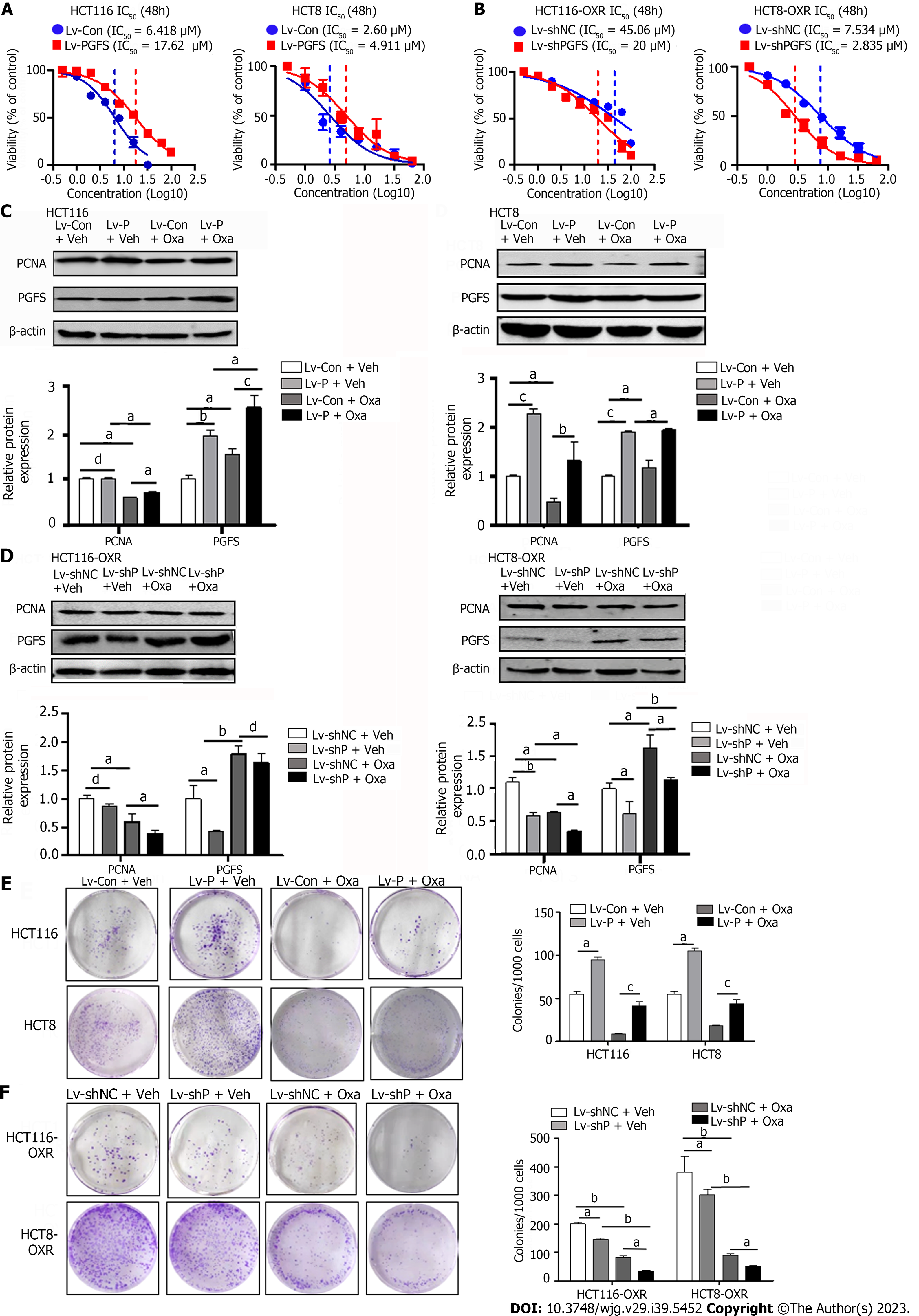
Figure 2 Prostaglandin F2α synthase resists the inhibitory effect of oxaliplatin on colorectal cancer cell proliferation.
A: The effects of prostaglandin F2α synthase (PGFS) overexpression on cell viability in HCT116 and HCT8 cells; B: The effects of PGFS knockdown on cell viability in HCT116-OxR and HCT8-OxR cells; C and D: Western blot analysis showed proliferating cell nuclear antigen levels in parental and oxaliplatin-resistant (OR) colorectal cancer (CRC) cells; E and F: Plate colony formation assay in parental and OR CRC cells. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dNo significance. PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PGFS: Prostaglandin F2α synthase; Oxa: Oxaliplatin; IC50: Half-inhibitory concentration.
- Citation: Wang YJ, Xie XL, Liu HQ, Tian H, Jiang XY, Zhang JN, Chen SX, Liu T, Wang SL, Zhou X, Jin XX, Liu SM, Jiang HQ. Prostaglandin F2α synthase promotes oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer through prostaglandin F2α-dependent and F2α-independent mechanism. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(39): 5452-5470
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i39/5452.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i39.5452