Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2023; 29(35): 5166-5177
Published online Sep 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5166
Published online Sep 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5166
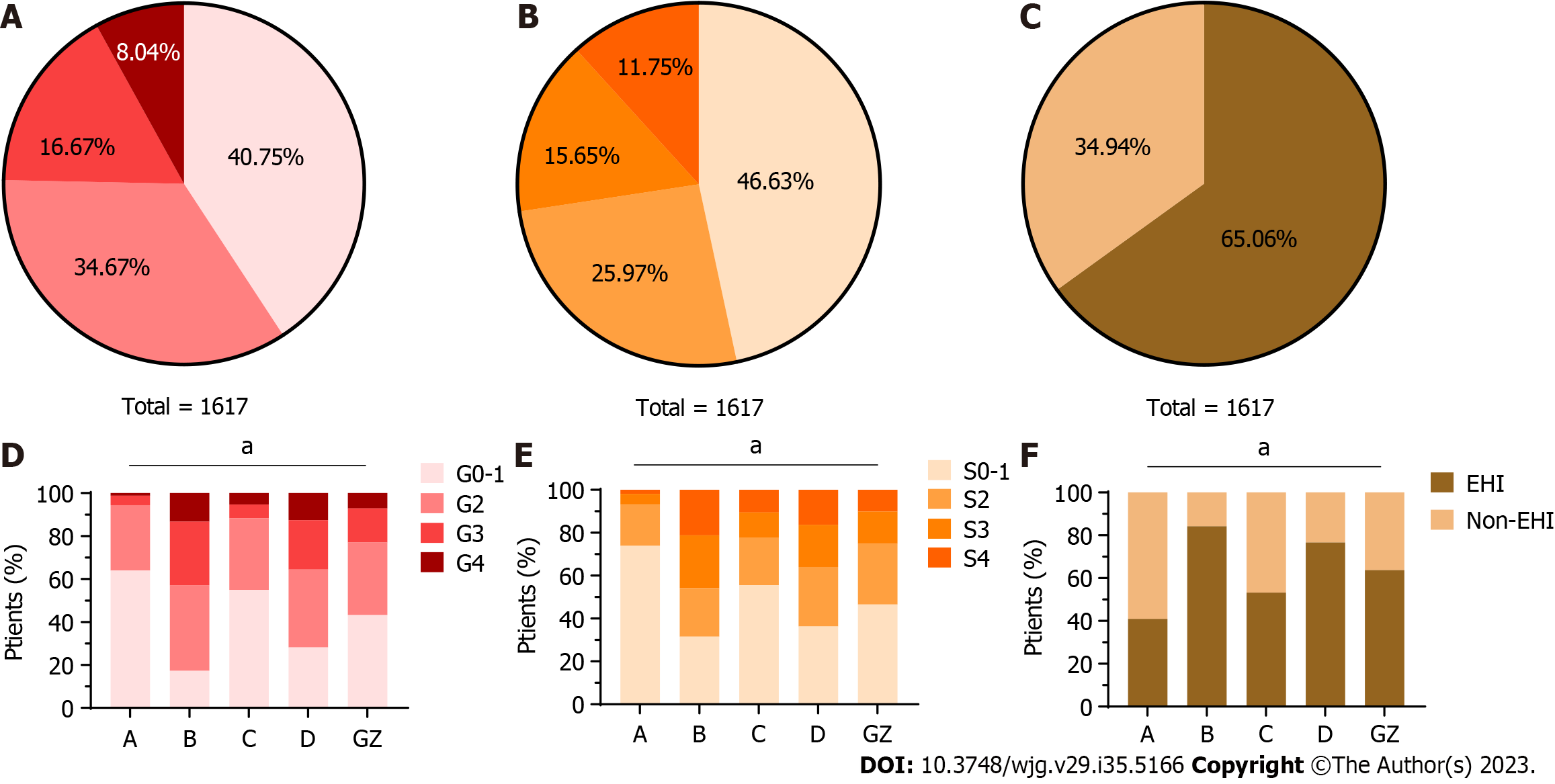
Figure 1 Distribution and liver histological features of chronic hepatitis B patients in different immune states.
A and D: Proportions of liver inflammation grades in different immune status groups; B and E: Proportions of fibrosis stages in different immune status groups; C and F: Proportions of significant hepatic injury in different immune status groups. A: HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection; B: HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B; C: HBeAg-negative chronic HBV infection; D: HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B; GZ: Grey zone; EHI: Evidenced hepatic injury. aP < 0.001.
- Citation: Yu HS, Jiang H, Li MK, Yang BL, Smayi A, Chen JN, Wu B, Yang YD. Lowering the threshold of alanine aminotransferase for enhanced identification of significant hepatic injury in chronic hepatitis B patients. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(35): 5166-5177
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i35/5166.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5166