Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2023; 29(35): 5154-5165
Published online Sep 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5154
Published online Sep 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5154
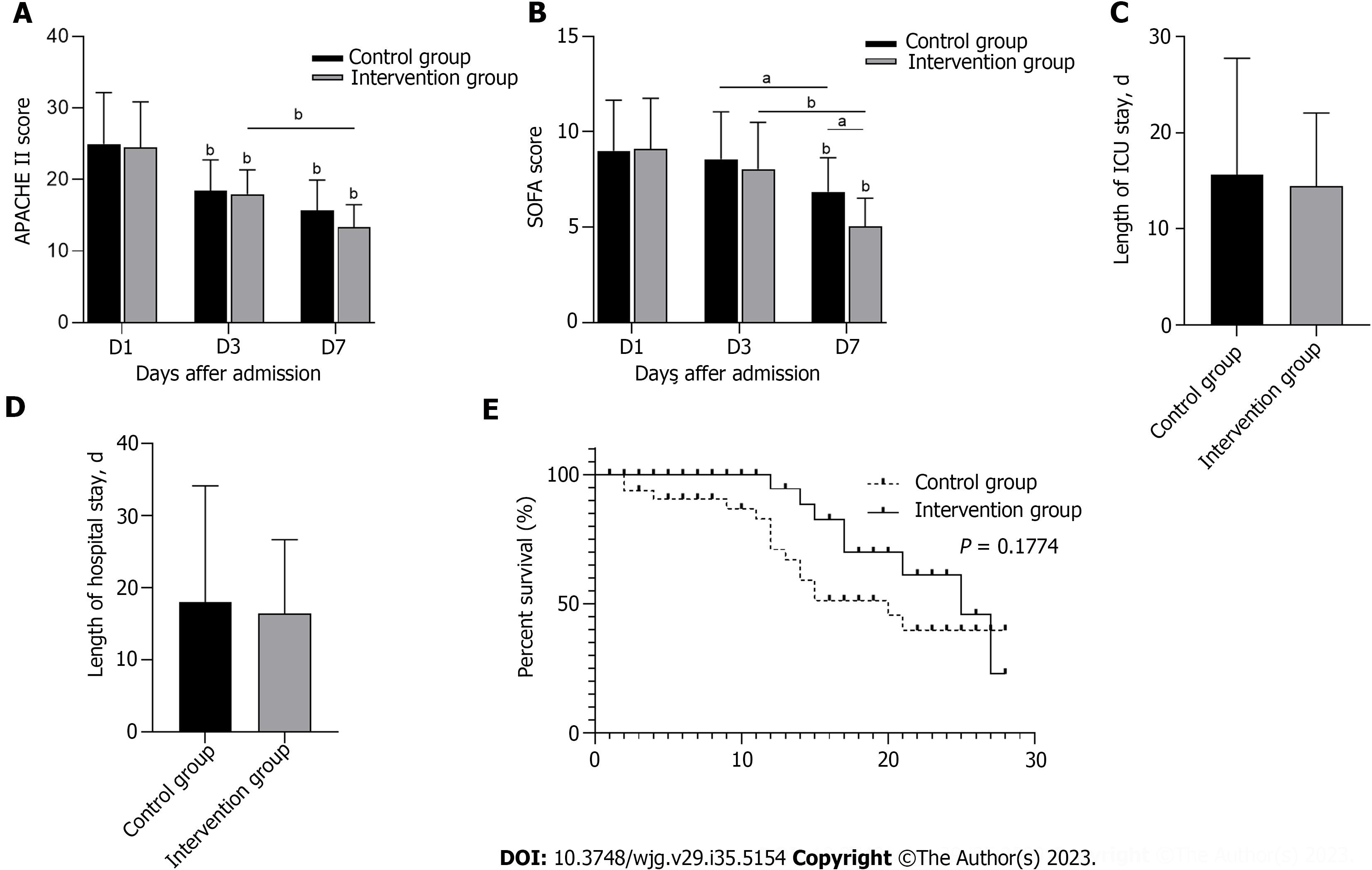
Figure 6 Comparisons of Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation score, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score, length of intensive care unit stay, length of hospital stay, and survival probability within 28 d between the two groups.
A: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation score; B: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score; C: Length of intensive care unit stay; D: Length of hospital stay; E: Survival probability within 28 d. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001. APACHE II: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; ICU: Intensive care unit.
- Citation: Chen TT, Lv JJ, Chen L, Li M, Liu LP. Heparanase inhibition leads to improvement in patients with acute gastrointestinal injuries induced by sepsis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(35): 5154-5165
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i35/5154.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5154