Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2023; 29(35): 5154-5165
Published online Sep 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5154
Published online Sep 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5154
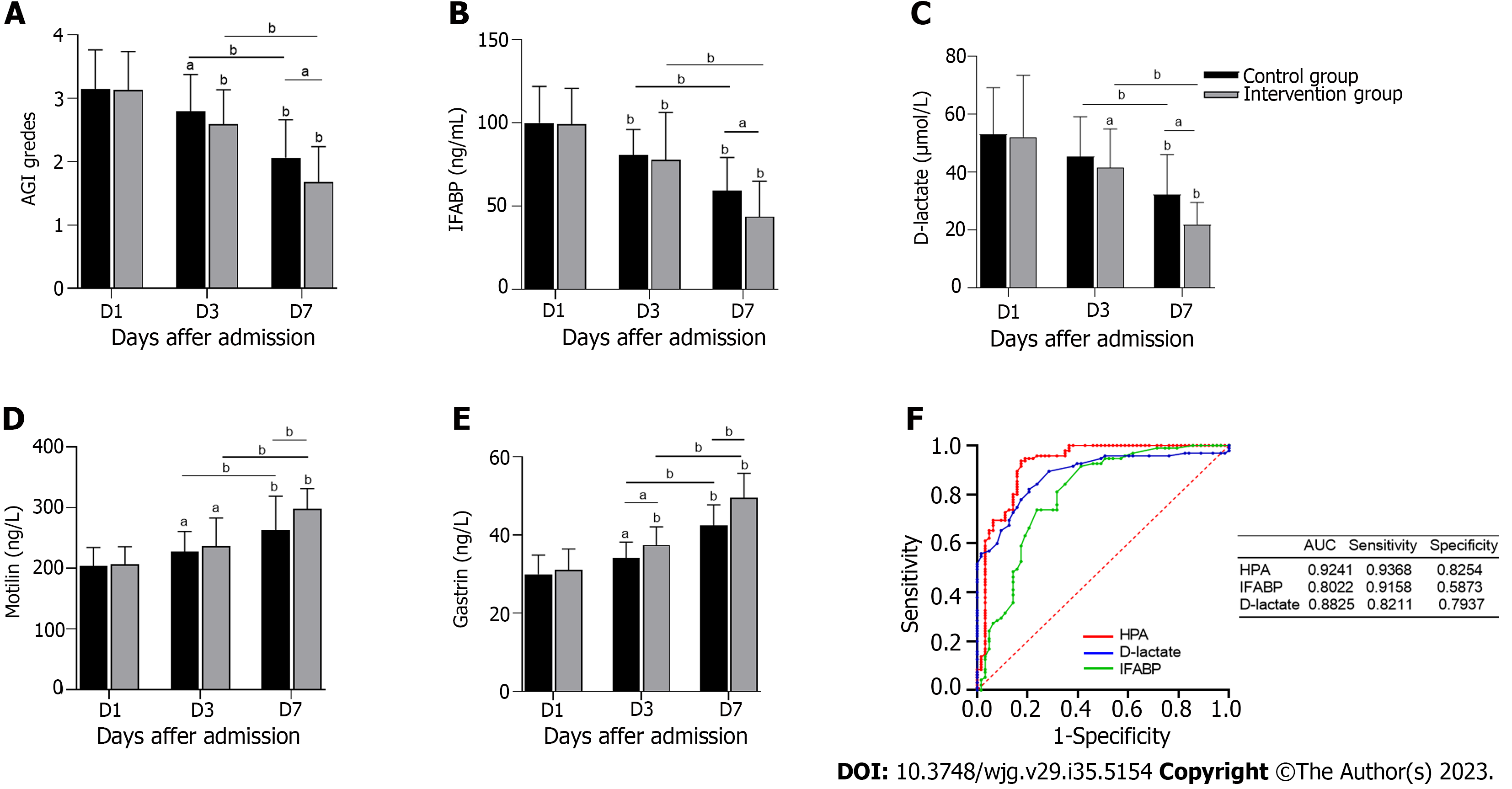
Figure 3 Comparisons of acute gastrointestinal injury grades, intestinal fatty acid binding protein, D-lactate, motilin, and gastrin levels between the two groups.
Receiver operating characteristic curves of heparanase, D-lactate and intestinal fatty acid binding protein. A: Acute gastrointestinal injury grades; B: Intestinal fatty acid binding protein; C: D-lactate; D: Motilin; E: Gastrin; F: Receiver operating characteristic curves of heparanase, D-lactate and intestinal fatty acid binding protein. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001. AGI: acute gastrointestinal injury; HPA: Heparanase; IFABP: Intestinal fatty acid binding protein; AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Chen TT, Lv JJ, Chen L, Li M, Liu LP. Heparanase inhibition leads to improvement in patients with acute gastrointestinal injuries induced by sepsis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(35): 5154-5165
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i35/5154.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5154