Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2023; 29(35): 5138-5153
Published online Sep 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5138
Published online Sep 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5138
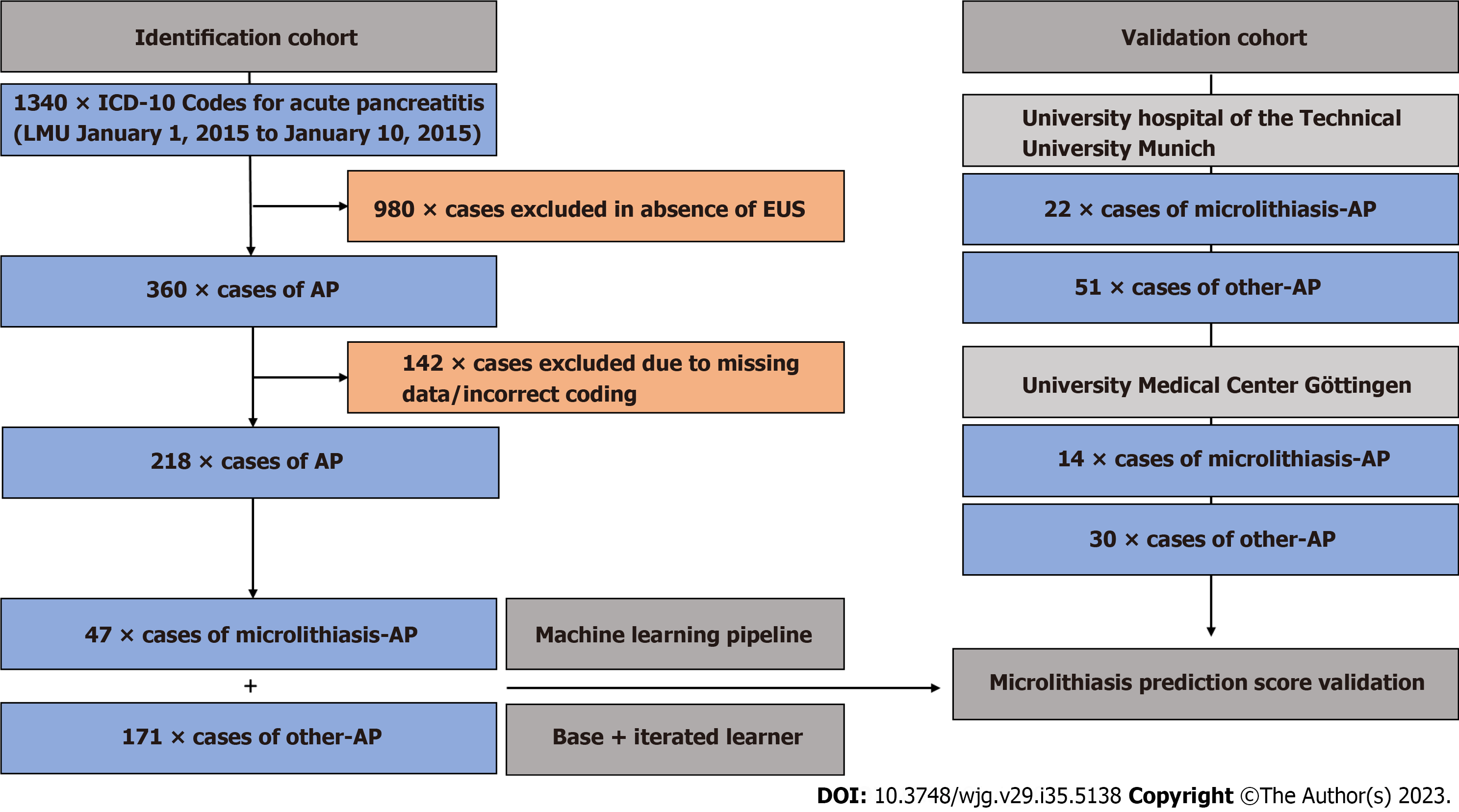
Figure 1 Flow chart for development and external independent validation of microlithiasis prediction score.
In the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität in Munich identification cohort, 218 acute pancreatitis patients treated as inpatients between 2015-2020 were included in the final machine learning-based score survey. The validation cohort, consisting of 117 pancreatitis cases, was composed of patient data from the University Hospital of Göttingen and Technical University Munich. The microlithiasis predictive model was trained using data from both biliary sludge and biliary microlithiasis patients to cover the entirety of biliary microconcrements and to reflect the current lack of uniform definitions of biliary sludge and biliary microlithiasis in clinical practice. EUS: Endosonography; AP: Acute pancreatitis.
- Citation: Sirtl S, Żorniak M, Hohmann E, Beyer G, Dibos M, Wandel A, Phillip V, Ammer-Herrmenau C, Neesse A, Schulz C, Schirra J, Mayerle J, Mahajan UM. Machine learning-based decision tool for selecting patients with idiopathic acute pancreatitis for endosonography to exclude a biliary aetiology. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(35): 5138-5153
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i35/5138.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i35.5138