Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2023; 29(33): 4991-5004
Published online Sep 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i33.4991
Published online Sep 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i33.4991
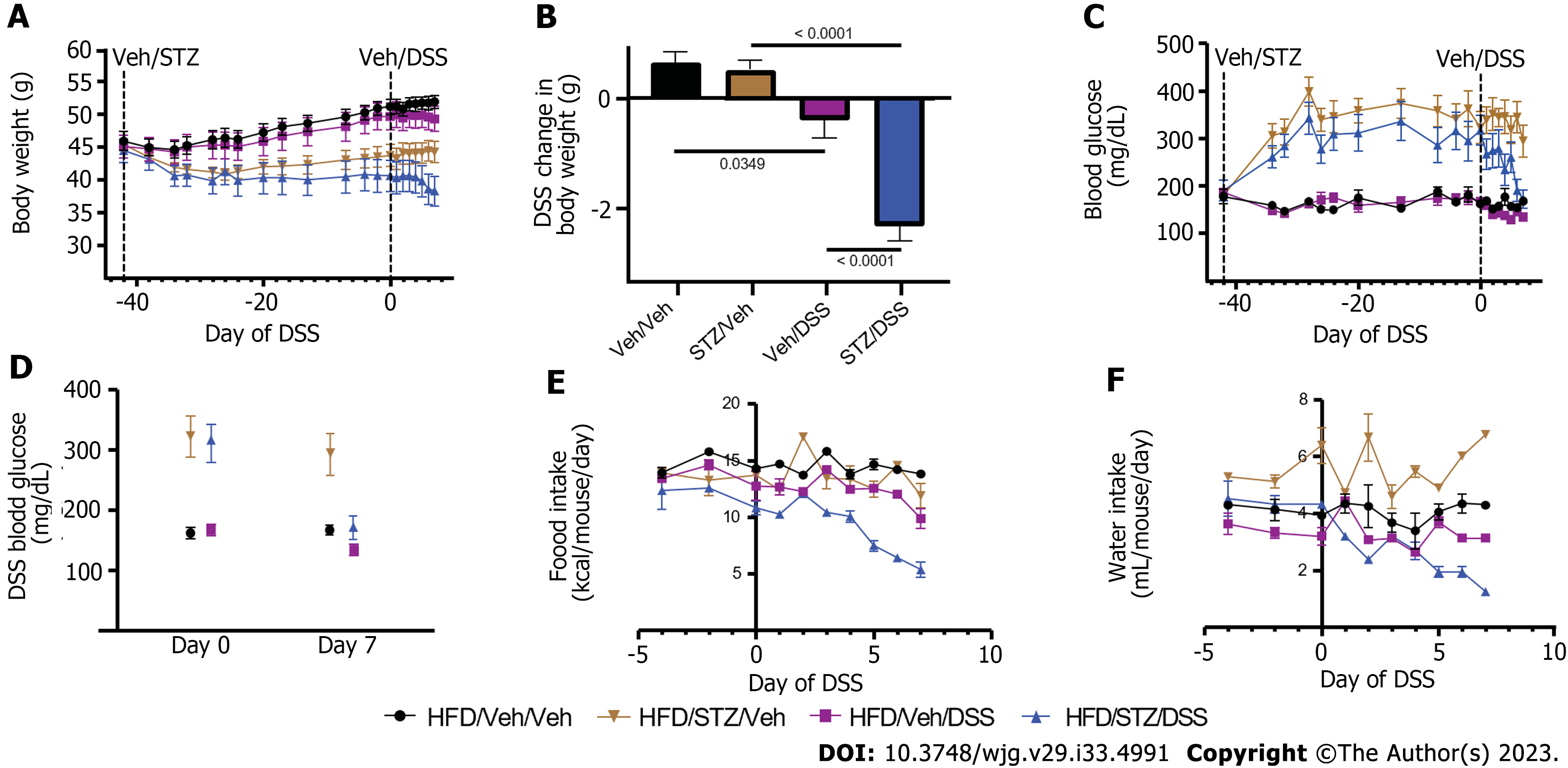
Figure 1 Body weight, blood glucose, food intake, and water consumption in diabetic diet-induced obese mice.
A: Body weight; B: Change in body weight during dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) course; C: Blood glucose; D: Change in blood glucose during the DSS course; E: Food intake; F: Water consumption in high-fat diet-fed, diet-induced obese mice that received either vehicle (Veh) or streptozotocin to induce hyperglycemia and subsequently received Veh or DSS in the drinking water for 7 d to induce colitis. n = 7-8 per group, mean ± standard error of the mean. DSS: Dextran sodium sulfate; Veh: Vehicle; STZ: Streptozotocin.
- Citation: Francis KL, Alonge KM, Pacheco MC, Hu SJ, Krutzsch CA, Morton GJ, Schwartz MW, Scarlett JM. Diabetes exacerbates inflammatory bowel disease in mice with diet-induced obesity. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(33): 4991-5004
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i33/4991.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i33.4991