Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2023; 29(32): 4860-4872
Published online Aug 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i32.4860
Published online Aug 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i32.4860
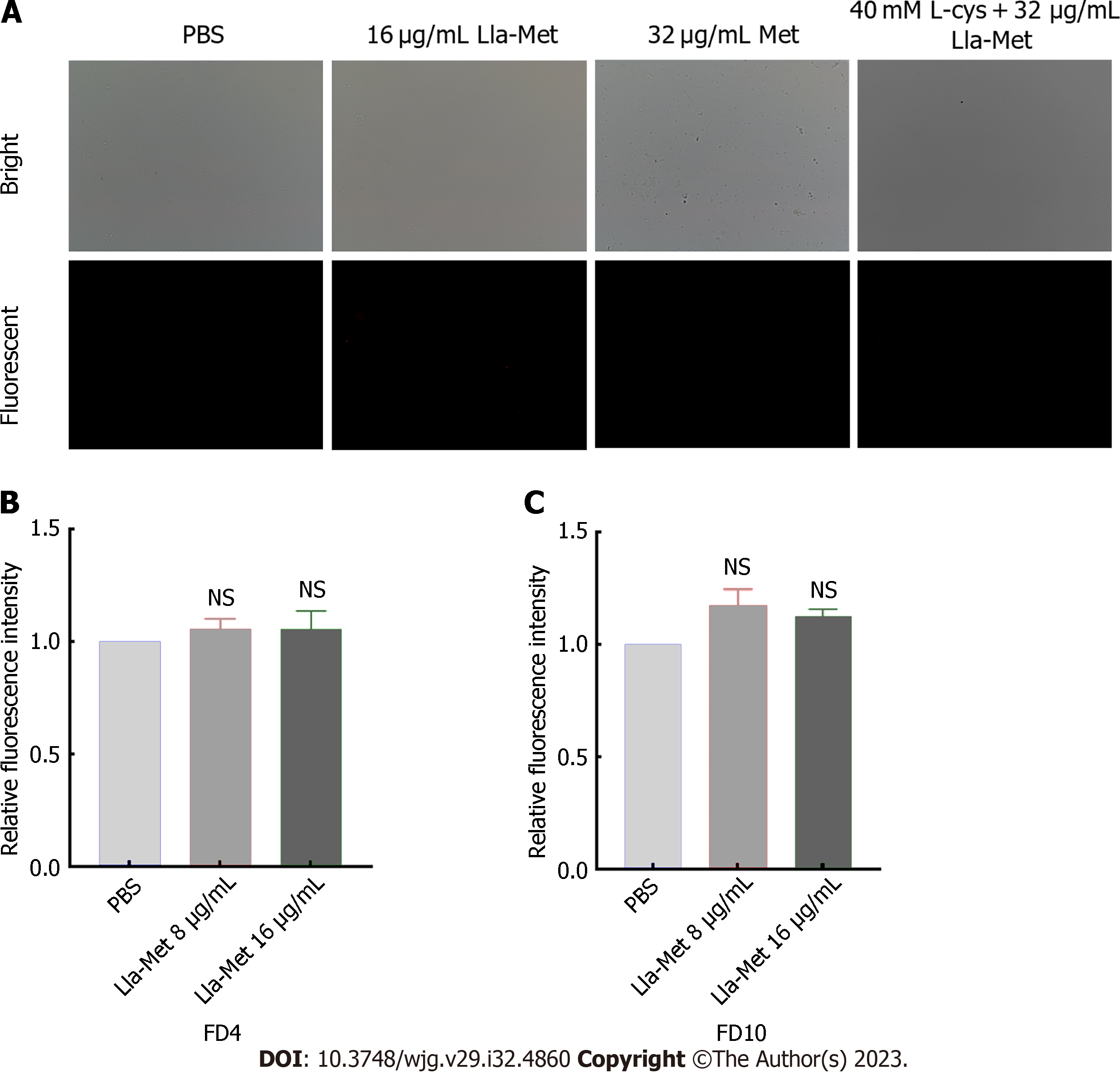
Figure 2 The effect of linolenic acid-metronidazole on cell membrane permeability.
A: Linolenic acid-metronidazole (Lla-met) induced membrane damages of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) using PI staining; B: Lla-met induced membrance pore size damage of H. pylori using FD4; C: Lla-met induced membrance pore size damage of H. pylori using FD10. PI, FD4 and FD10 can’t pass through the intact cell membrane. NS: Not significant; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; Lla-Met: Linolenic acid-metronidazole.
- Citation: Zhou WT, Dai YY, Liao LJ, Yang SX, Chen H, Huang L, Zhao JL, Huang YQ. Linolenic acid-metronidazole inhibits the growth of Helicobacter pylori through oxidation. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(32): 4860-4872
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i32/4860.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i32.4860