Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2023; 29(31): 4744-4762
Published online Aug 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i31.4744
Published online Aug 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i31.4744
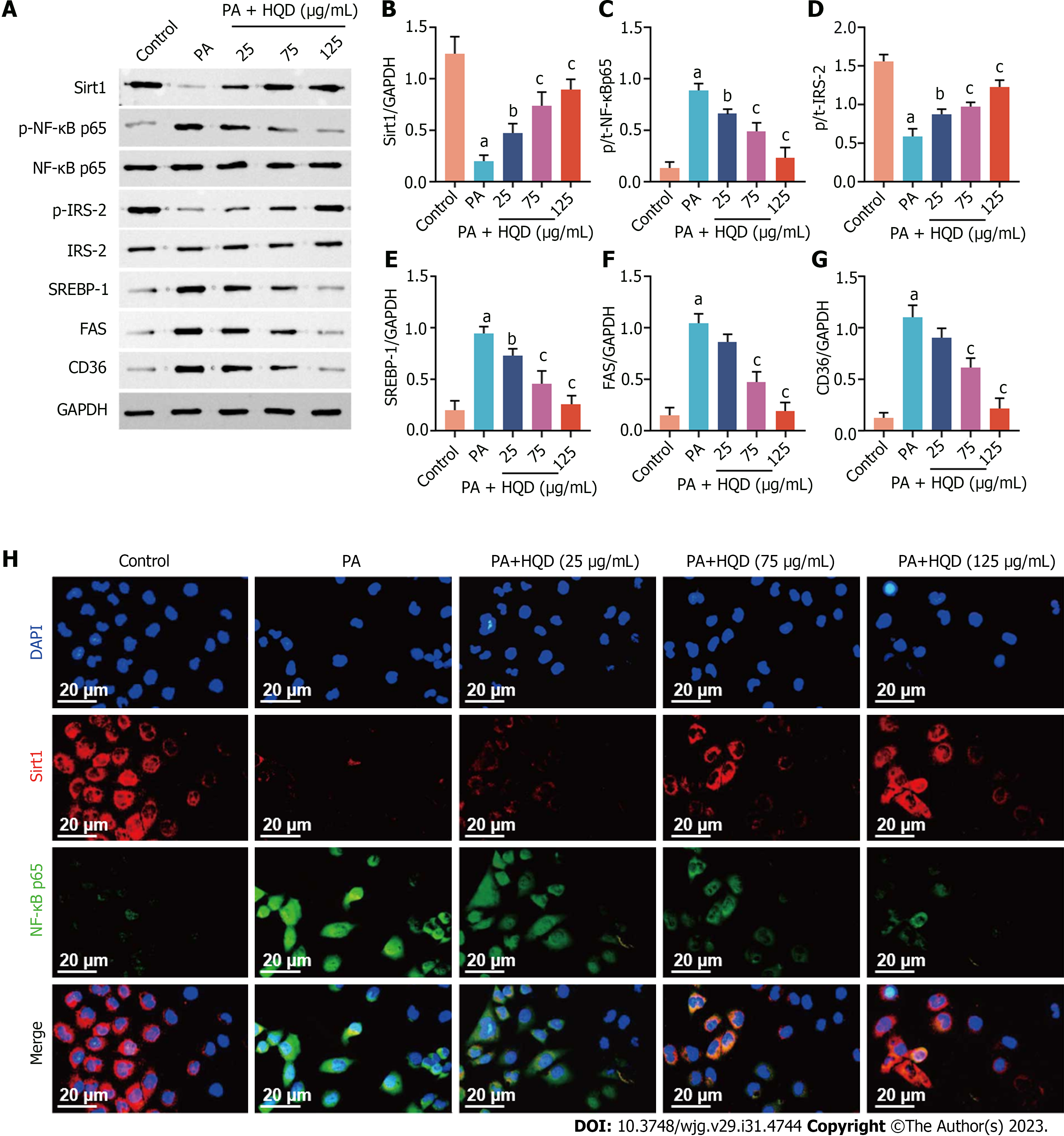
Figure 7 Huangqin decoction activates the Sirt1/NF-κB pathway in palmitic acid-induced HepG2 cells.
Data are presented as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. aP < 0.01 vs the control group, bP < 0.05 and cP < 0.01 vs the palmitic acid group. A: Expression levels of Sirt1, p-NF-κB/NF-κB, p-IRS-2/IRS-2, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1, fatty acid synthase, and cluster of differentiation 36 in HepG2 cells; B–G: Semi-quantitative analysis of these proteins; H: Representative images of immunofluorescent staining of Sirt1 and NF-κB in HepG2 cells. CD36: Cluster of differentiation 36; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HQD, Huangqin decoction; PA: Palmitic acid; SREBP: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein.
- Citation: Yan BF, Pan LF, Quan YF, Sha Q, Zhang JZ, Zhang YF, Zhou LB, Qian XL, Gu XM, Li FT, Wang T, Liu J, Zheng X. Huangqin decoction alleviates lipid metabolism disorders and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by triggering Sirt1/NF-κB pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(31): 4744-4762
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i31/4744.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i31.4744