Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2023; 29(31): 4744-4762
Published online Aug 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i31.4744
Published online Aug 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i31.4744
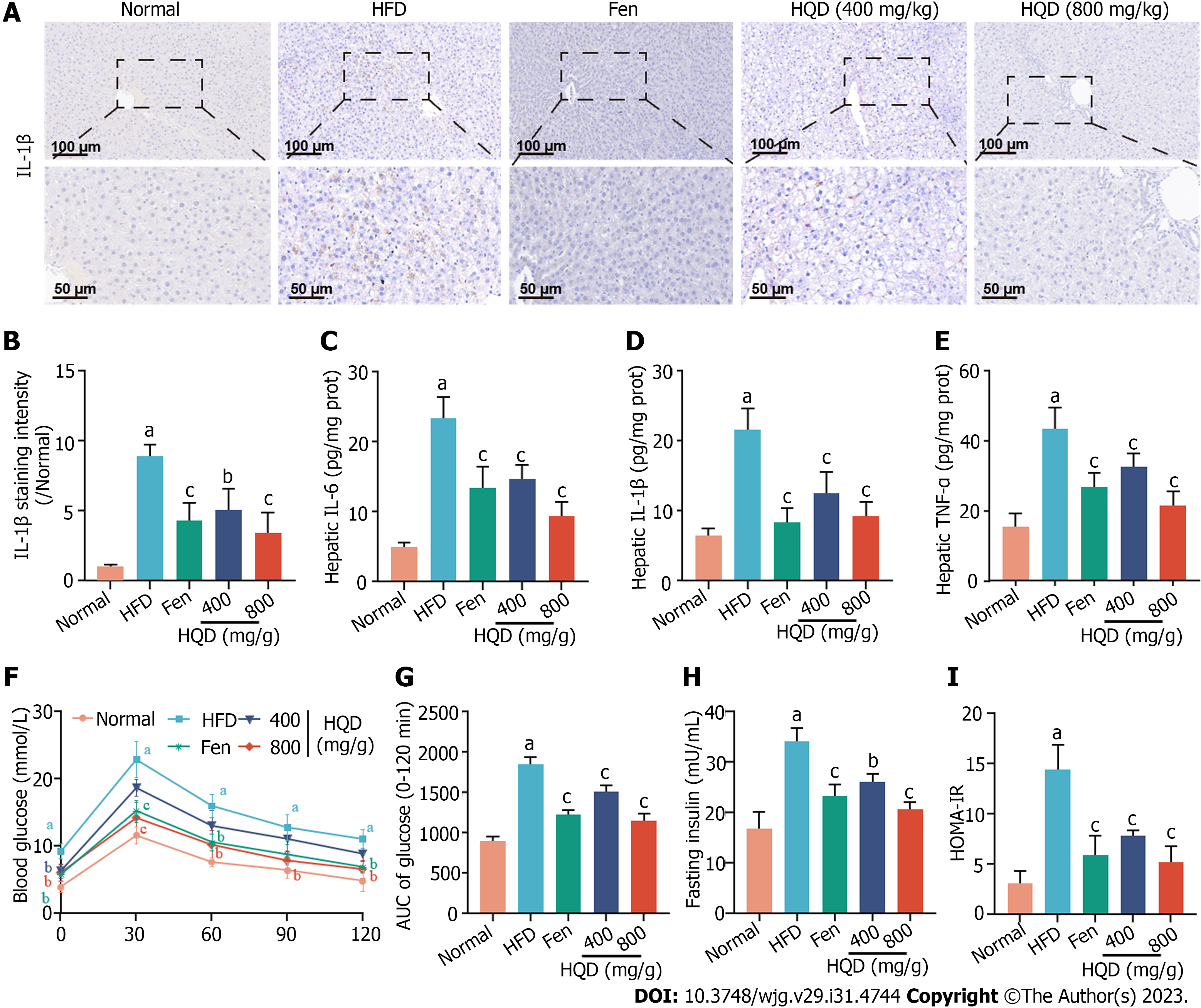
Figure 4 Huangqin decoction suppresses hepatic inflammation and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rats.
Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 4–8). aP < 0.01 vs the normal group, bP < 0.05 and cP < 0.01 vs the high-fat diet (HFD) group. A: Representative images of immunohistochemical staining of interleukin (IL)-1β in liver sections; B: Quantitative analysis of staining intensity of IL-1β; C-E: Levels of IL-6 (C), IL-1β (D), and tumor necrosis factor-α (E) in the liver of HFD-fed rats; F: Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT); G: Area under the curve from OGTT; H: Level of fasting serum insulin; I: Values of homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance. AUC: Area under the curve; Fen: Fenofibrate; HFD: High-fat diet; HOMA-IR: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HQD: Huangqin decoction; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Yan BF, Pan LF, Quan YF, Sha Q, Zhang JZ, Zhang YF, Zhou LB, Qian XL, Gu XM, Li FT, Wang T, Liu J, Zheng X. Huangqin decoction alleviates lipid metabolism disorders and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by triggering Sirt1/NF-κB pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(31): 4744-4762
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i31/4744.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i31.4744