Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2023; 29(30): 4642-4656
Published online Aug 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i30.4642
Published online Aug 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i30.4642
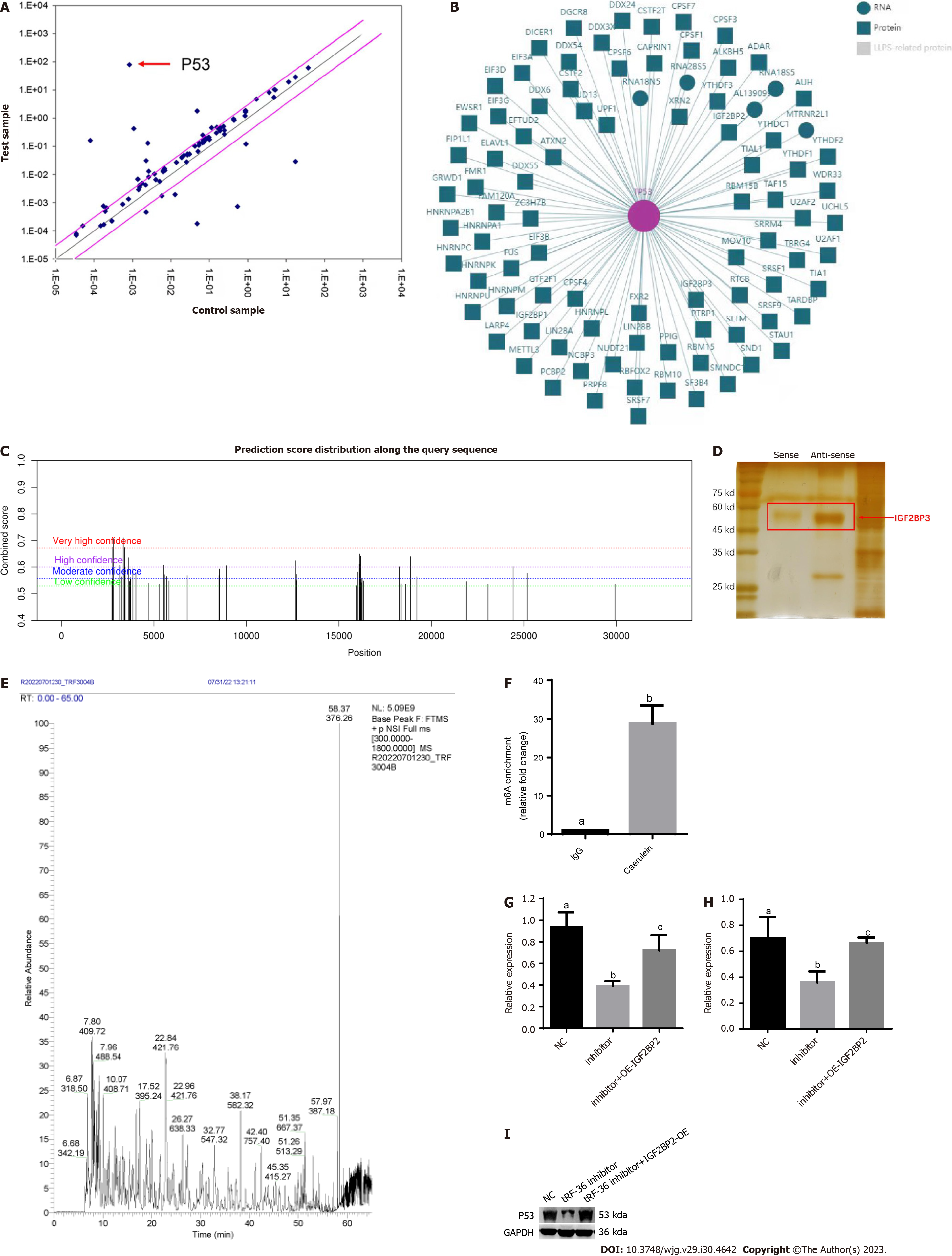
Figure 5 Exploration of the molecular mechanisms of tRNA-derived fragments 36 in acute pancreatitis progression.
A: p53 was the most significantly downregulated gene in ferroptosis gene microarray analysis after tRNA-derived fragments 36 (tRF-36) knockdown; B: The interaction network of p53 and m6A proteins; C: The m6A modification analysis for p53 mRNA by SRAMP; D: The RNA pull down assay for tRF-36 with insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3; E: Mass spectrometry results for tRF-36; F: The level of m6A modification of p53 by methylated RNA immunoprecipitation-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.; G: The p53 expression level after the knockdown of tRF-36 by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction; H: The p53 expression level after the knockdown of tRF-36 by western blot; I: The changes in P53 expression. a, b, and c represent different expression levels, the same letter represents no significant difference between groups (P > 0.05), different letters represent significant difference between groups (P < 0.05). tRF-36: tRNA-derived fragments 36; NC: Normal control; IgG: Immunoglobulin G; OE: Overexpression; IGF2BP3: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3.
- Citation: Fan XR, Huang Y, Su Y, Chen SJ, Zhang YL, Huang WK, Wang H. Exploring the regulatory mechanism of tRNA-derived fragments 36 in acute pancreatitis based on small RNA sequencing and experiments. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(30): 4642-4656
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i30/4642.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i30.4642