Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2023; 29(26): 4120-4135
Published online Jul 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i26.4120
Published online Jul 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i26.4120
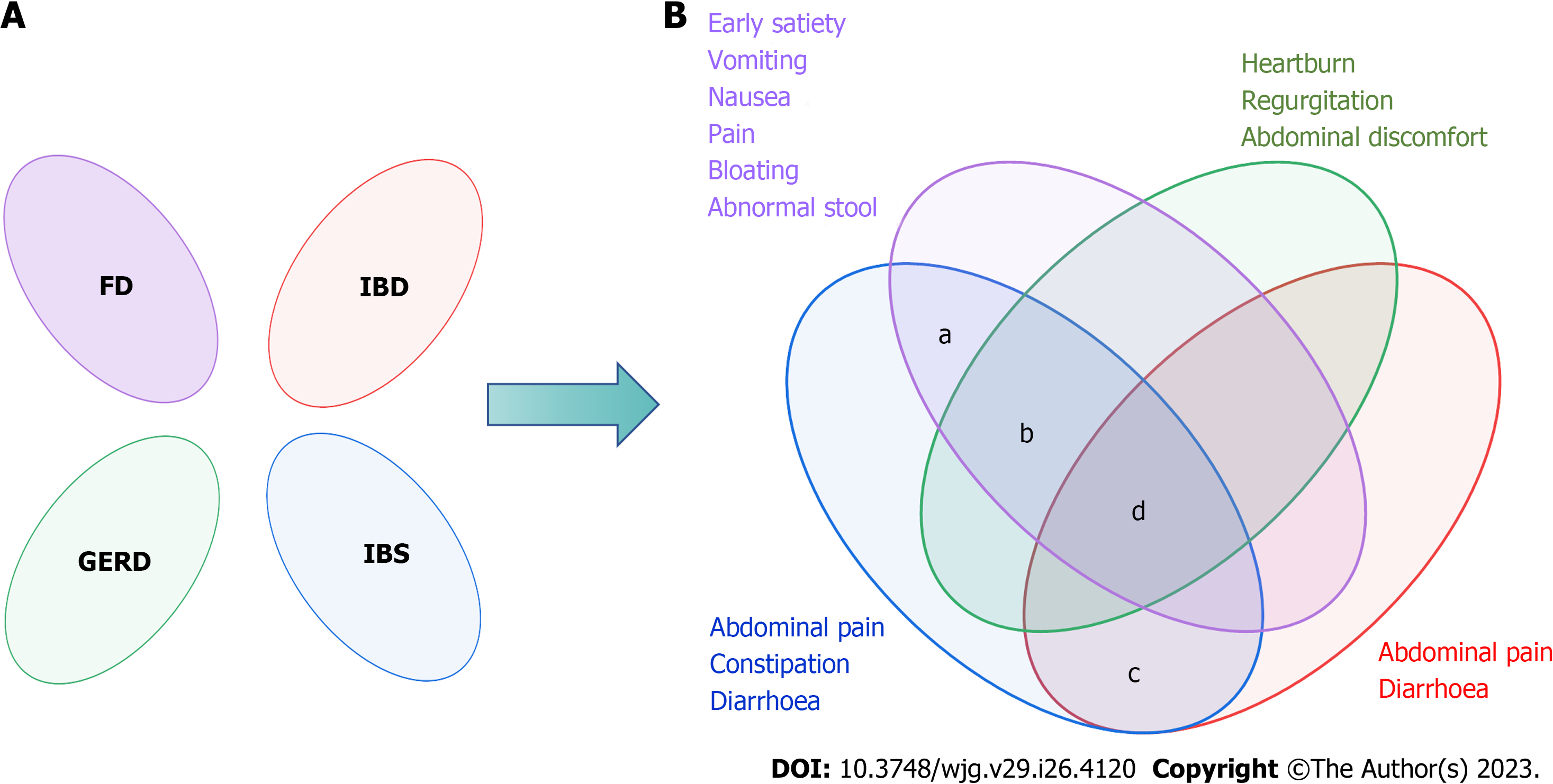
Figure 2 The Rome Foundation's views on the overlap of functional gastrointestinal diseases.
A: Rome I considered the functional bowel disorders to be independent diseases; B: Rome II and Rome III recognized there was overlap between functional gastrointestinal diseases. a: The prevalence of overlap between irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and functional dyspepsia was 55.3%; b: The overlap between IBS and gastroesophageal reflux disease ranged from 3%-79% in the questionnaire and 10%-74% when diagnosed by endoscopy; c: A 2020 meta-analysis showed that the pooled prevalence of IBS-type symptoms was 32.5%; d: Only 2.3% had esophageal, gastroduodenal, bowel, and anorectal overlap. FD: Functional dyspepsia; IBD: Inflammatory bowel diseases; GERD: Gastroesophageal reflux disease; IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Citation: Huang KY, Wang FY, Lv M, Ma XX, Tang XD, Lv L. Irritable bowel syndrome: Epidemiology, overlap disorders, pathophysiology and treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(26): 4120-4135
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i26/4120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i26.4120