Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2023; 29(25): 4053-4071
Published online Jul 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i25.4053
Published online Jul 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i25.4053
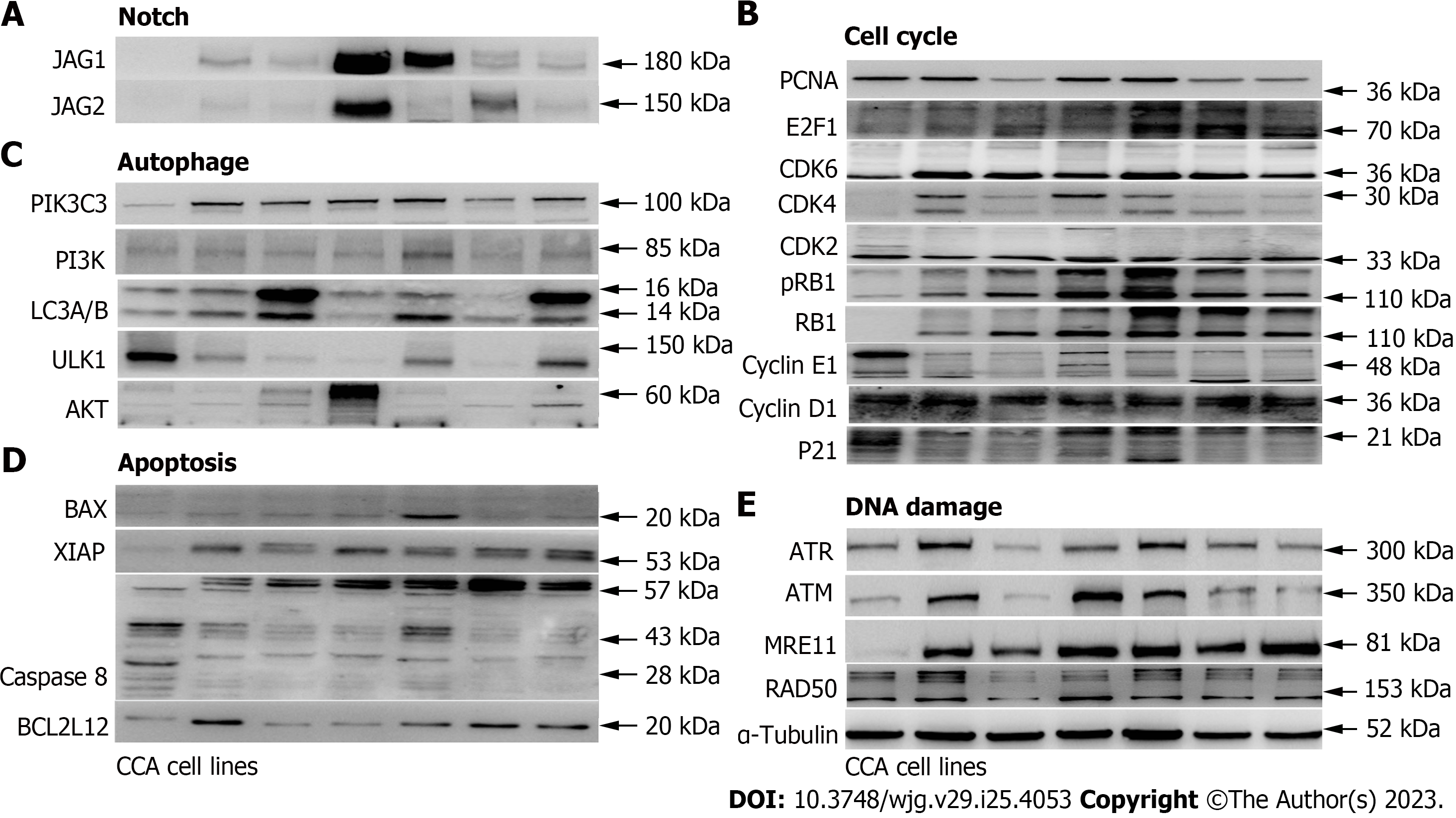
Figure 3 The cell cycle and Notch pathway associated protein expression levels are up-regulated in cholangiocarcinoma cell lines compared to the normal human bile duct cells.
The protein expression levels of leading-edge genes from (A) Notch, (B) cell cycle, (C) autophagy, (D) cell death, and (E) DNA damage were determined in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cell lines compared to hBD. Several cell cycle and Notch associated genes, including CDK4, CDK6, E2F1, JAG1, and JAG2, were up-regulated in CCA cell lines. CCA tumor cell lines including HuCCT1, ETK-1, H1, RBE, TFK-1 and SSP25. α-Tubulin served as the loading control.
- Citation: Liu D, Shi Y, Chen H, Nisar MA, Jabara N, Langwinski N, Mattson S, Nagaoka K, Bai X, Lu S, Huang CK. Molecular profiling reveals potential targets in cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(25): 4053-4071
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i25/4053.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i25.4053