Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2023; 29(24): 3793-3806
Published online Jun 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i24.3793
Published online Jun 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i24.3793
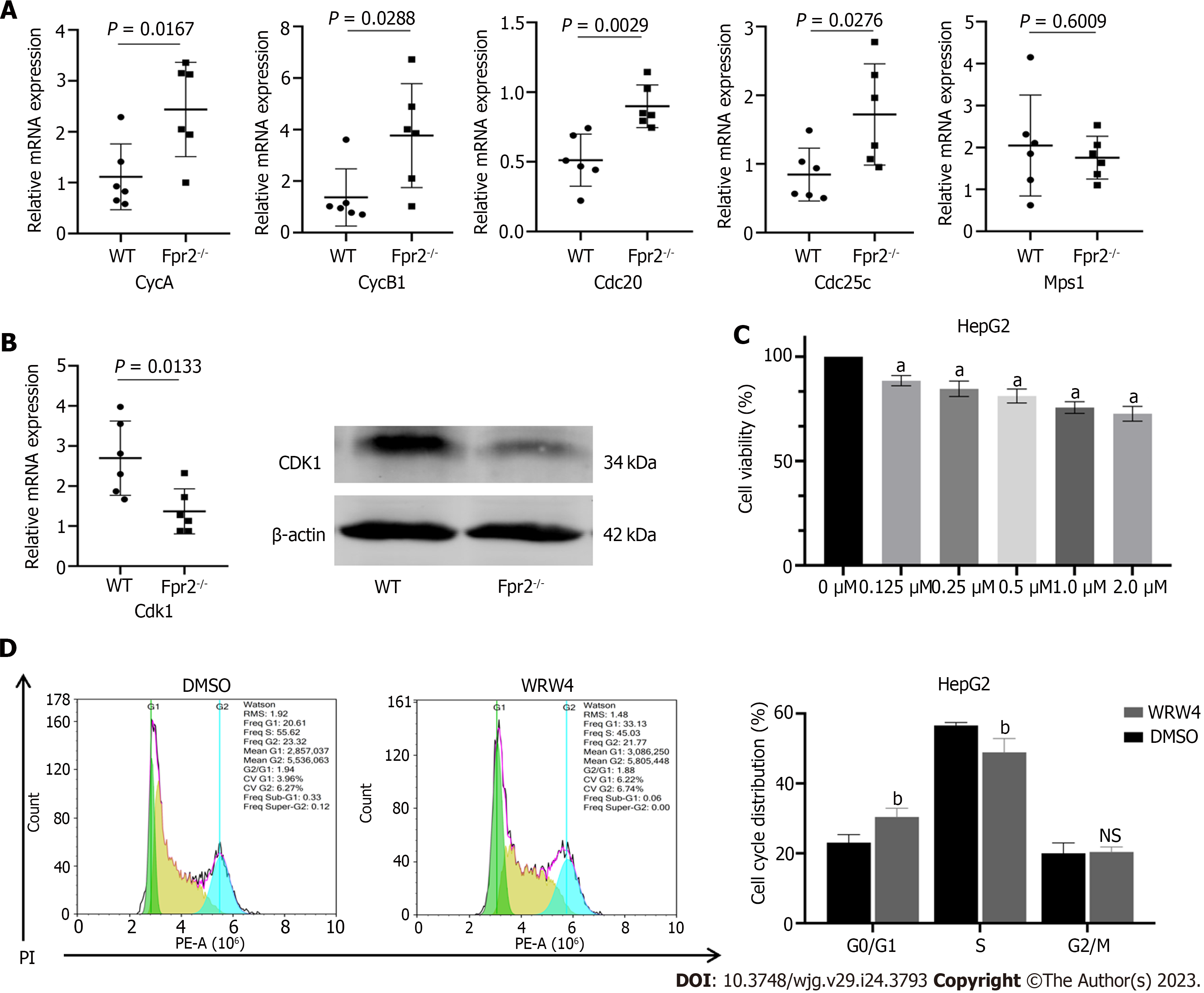
Figure 4 The effect of formyl peptide receptor 2 deletion on cell cycle.
A: Quantitative real time-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) validates the expression of key cell cycle genes regulated by formyl peptide receptor 2 (Fpr2), including CycA, CycB1, Cdc20, Cdc25c, and Mps1 (n = 6). P values are indicated on the graphs; B: qRT-PCR and western blot analyses are used to validate the changes in expression of CDK1; C: The effect of different concentrations of WRW4 on the proliferation activity of HepG2 cells detected by CCK-8 (n = 5); D: The cell cycle distribution of HepG2 cells treated with WRW4 (1 μM) and dimethyl sulfoxide determined by flow cytometry (n = 3). Data are shown as mean ± SD. aP < 0.0001 vs the 0 μM group; bP < 0.05 vs the dimethyl sulfoxide group; NS: No significant; Fpr2: Formyl peptide receptor 2; WT: Wild-type; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide.
- Citation: Liu H, Sun ZY, Jiang H, Li XD, Jiang YQ, Liu P, Huang WH, Lv QY, Zhang XL, Li RK. Transcriptome sequencing and experiments reveal the effect of formyl peptide receptor 2 on liver homeostasis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(24): 3793-3806
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i24/3793.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i24.3793