Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2023; 29(24): 3770-3792
Published online Jun 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i24.3770
Published online Jun 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i24.3770
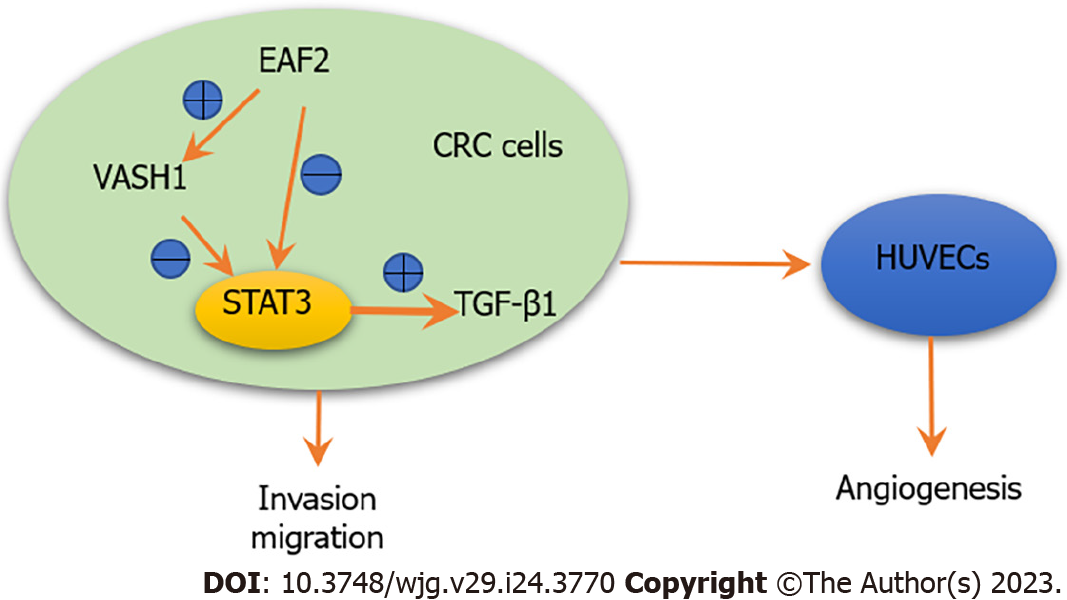
Figure 11 Schematic depiction of ELL-associated factor 2 and vasohibin 1 regulating the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3/ transforming growth factor-β1 signaling pathway in this study.
Overexpression of ELL-associated factor 2 may inhibit the activity of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3/transforming growth factor-β1 pathway by up-regulating the expression of vasohibin 1, thereby inhibiting cell invasion, migration and angiogenesis. EAF2: ELL-associated factor 2; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-β1; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; CRC: Colorectal cancer; HUVECs: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells; VASH1: Vasohibin 1.
- Citation: Feng ML, Sun MJ, Xu BY, Liu MY, Zhang HJ, Wu C. Mechanism of ELL-associated factor 2 and vasohibin 1 regulating invasion, migration, and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(24): 3770-3792
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i24/3770.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i24.3770