Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2023; 29(22): 3422-3439
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3422
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3422
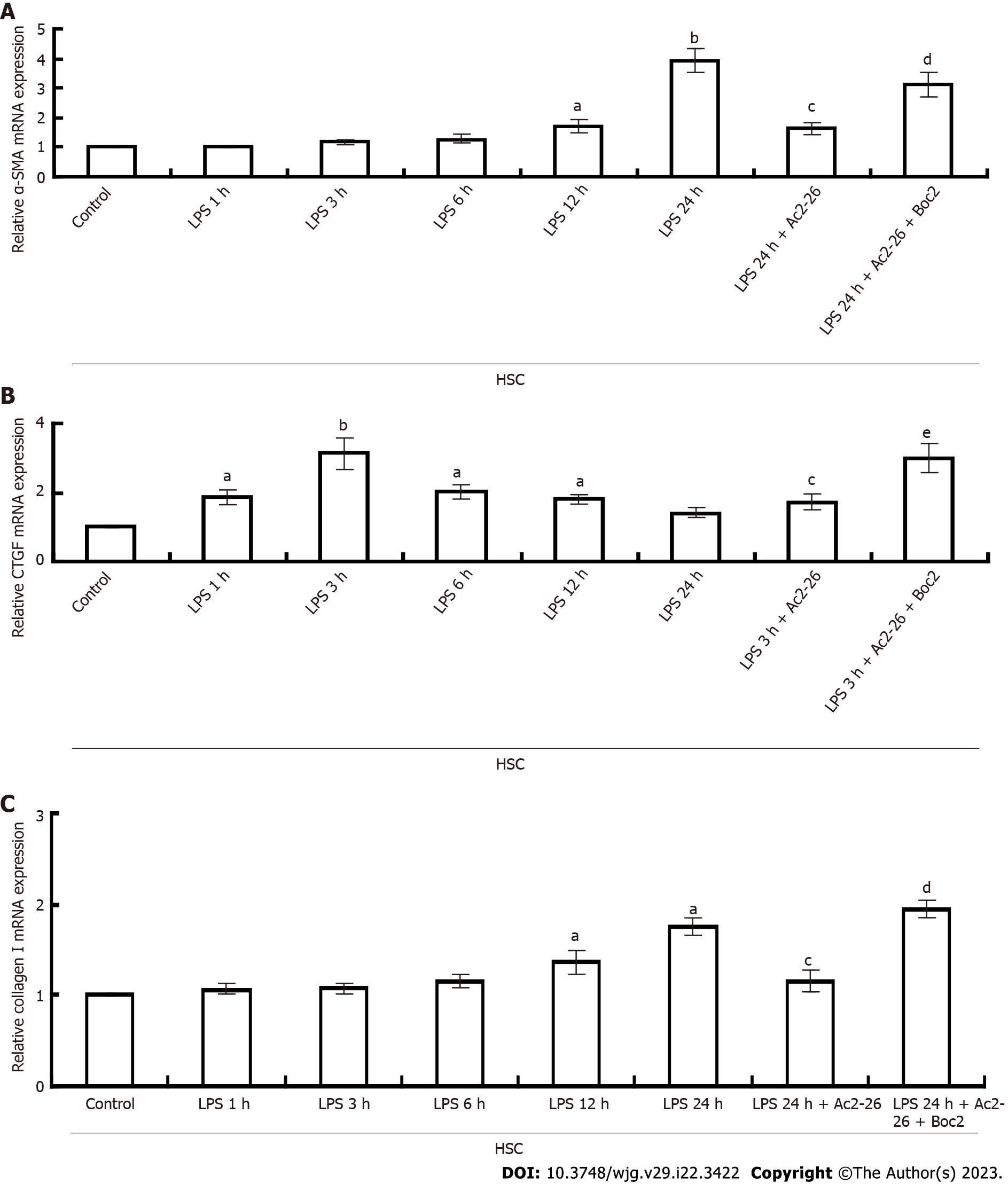
Figure 5 Annexin A1 inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation.
A: Changes in α-smooth muscle actin expression in hepatic stellate cell; B: Connective tissue growth factor mRNA was quantified using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; C: Collagen I mRNA expression. GAPDH was used as an internal control. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs controls; cP < 0.05 vs lipopolysaccharide; dP < 0.05 and eP < 0.01 vs lipopolysaccharide + Ac2-26 (n = 8). AnxA1: Annexin A1; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; CTGF: Connective tissue growth factor; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; Ac2-26: Active N-terminal peptide of AnxA1; Boc2: N-formyl peptide receptor antagonist N-Boc-Phe-Leu-Phe-Leu-Phe.
- Citation: Fan JH, Luo N, Liu GF, Xu XF, Li SQ, Lv XP. Mechanism of annexin A1/N-formylpeptide receptor regulation of macrophage function to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(22): 3422-3439
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i22/3422.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3422