Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2023; 29(22): 3385-3399
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3385
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3385
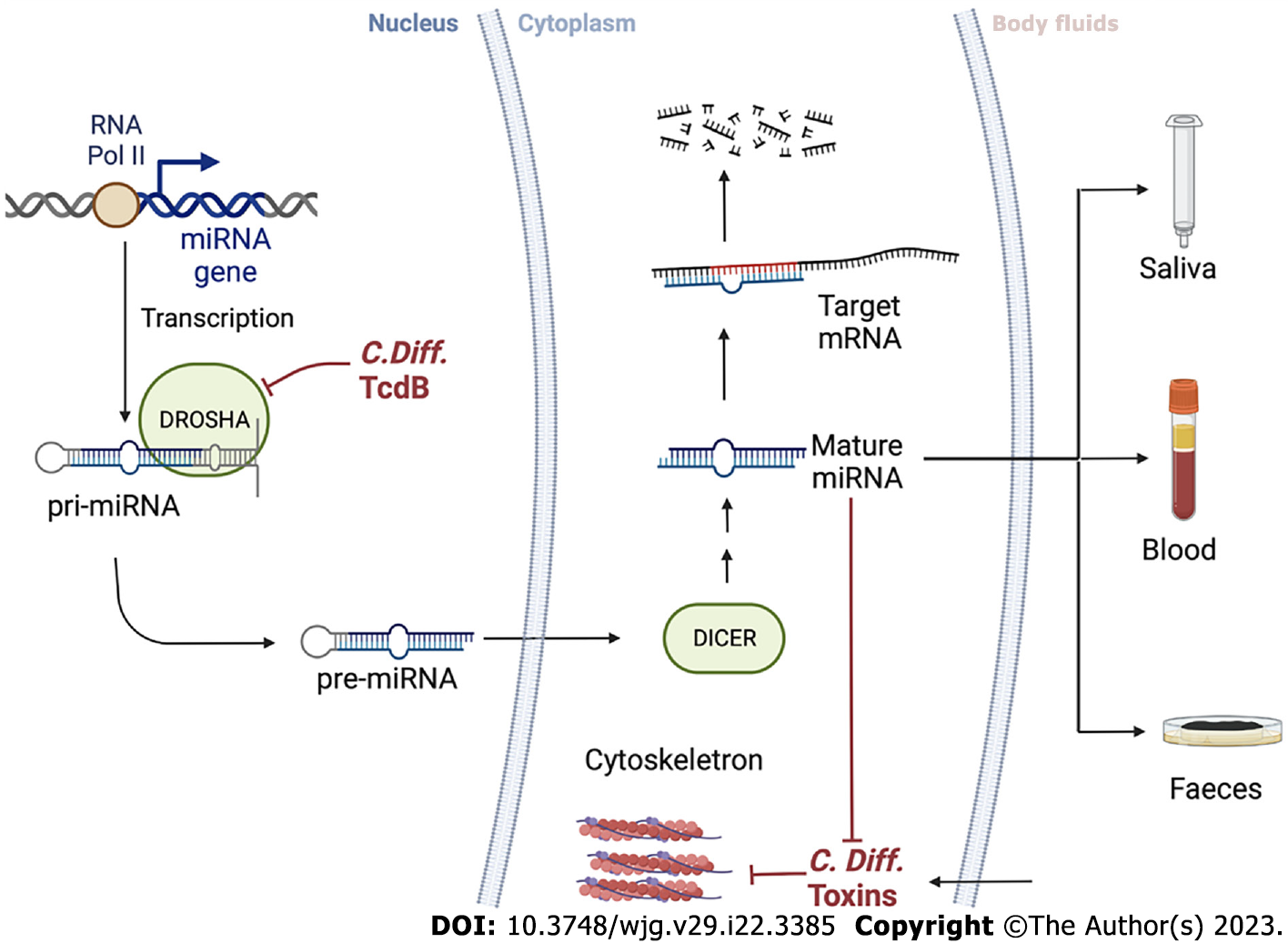
Figure 4 Clostridioidesdifficile and microRNAs cross-interact inside the cells.
microRNA (miRNA) is a small single-stranded RNA that plays a key role in gene expression regulation. It starts in the cell nucleus, where primary miRNAs are produced by RNA Pol II through miRNA transcription from DNA sequences or miRNA genes. Precursor miRNA, around 60-110 nucleotides long transcripts with a shorter stem-loop structure, are produced from primary miRNAs by RNase type III (DROSHA) enzyme with several maturation processes and is then transported to the cytoplasm via DICER. Toxin B from Clostridioides difficile may interfere with DROSHA function. A fraction of miRNA binding specific sequences (2-8 nucleotides long) can pair with miRNA response elements in the 3’ untranslated region of the target mRNA, causing translational repression and degradation of the target mRNA. Thus, miRNA expression patterns can indicate non-physiological events such as Clostridioides difficile infection. By detecting changes in miRNA patterns in body fluids, such as saliva, blood, and stool, the screening accuracy can be improved. miRNA: microRNA; pri-miRNA: Primary miRNA; pre-miRNA: Precursor miRNA; C. difficile: Clostridioides difficile.
- Citation: Bocchetti M, Ferraro MG, Melisi F, Grisolia P, Scrima M, Cossu AM, Yau TO. Overview of current detection methods and microRNA potential in Clostridioides difficile infection screening. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(22): 3385-3399
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i22/3385.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3385