Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2023; 29(22): 3385-3399
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3385
Published online Jun 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3385
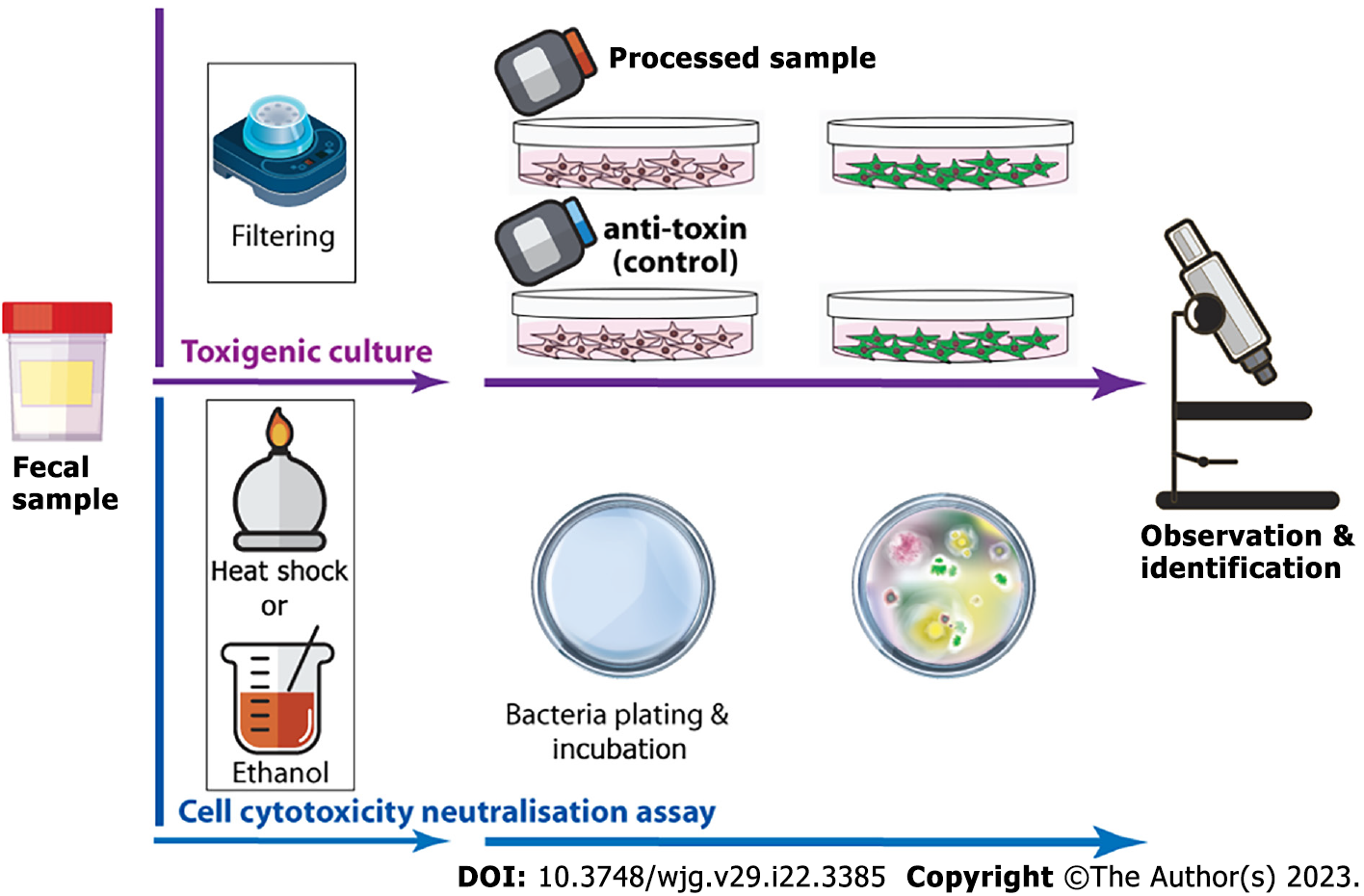
Figure 3 Idealised summary of toxigenic culture and cell cytotoxicity neutralisation assay for Clostridioidesdifficile infection identification.
In toxigenic culture, the faecal sample is first exposed to heat shock or alcohol shock to kill Clostridioides difficile (C. difficile) and other microorganisms, and heat/alcohol resistant spores of C. difficile survive. The sample is then plated on selective agar and incubated anaerobically at 37 °C for at least 48 h to observe and confirm the colonisation of C. difficile. For the cell cytotoxicity neutralisation assay, the faecal sample is filtered and added to a toxin-sensitive cell line with/without antiserum. After 24-48 h of incubation, the cytopathological effect is then examined microscopically.
- Citation: Bocchetti M, Ferraro MG, Melisi F, Grisolia P, Scrima M, Cossu AM, Yau TO. Overview of current detection methods and microRNA potential in Clostridioides difficile infection screening. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(22): 3385-3399
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i22/3385.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i22.3385