Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2023; 29(20): 3119-3132
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3119
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3119
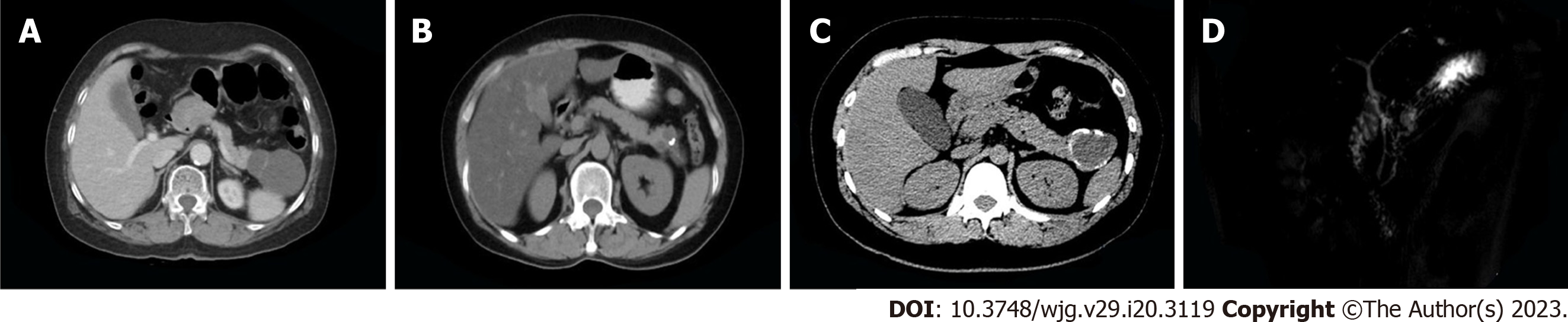
Figure 1 Representative radiographic images showing the mucinous cystic neoplasms.
A: Computed tomography (CT) scan showing a cystic neoplasm in the pancreatic tail with a clear boundary and linear separation within the lesion; B: CT scan showing multilocular cysts with a slightly high-density solid component, thickened septa, and punctate calcifications; C: CT scan showing a cyst with a slightly thickened cyst wall and multiple calcification foci; D: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showing mixed signals of the mass and the dilatation of the nearby pancreatic duct.
- Citation: Xia Q, Li F, Min R, Sun S, Han YX, Feng ZZ, Li N. Malignancy risk factors and prognostic variables of pancreatic mucinous cystic neoplasms in Chinese patients. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(20): 3119-3132
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i20/3119.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3119