Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2023; 29(20): 3103-3118
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3103
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3103
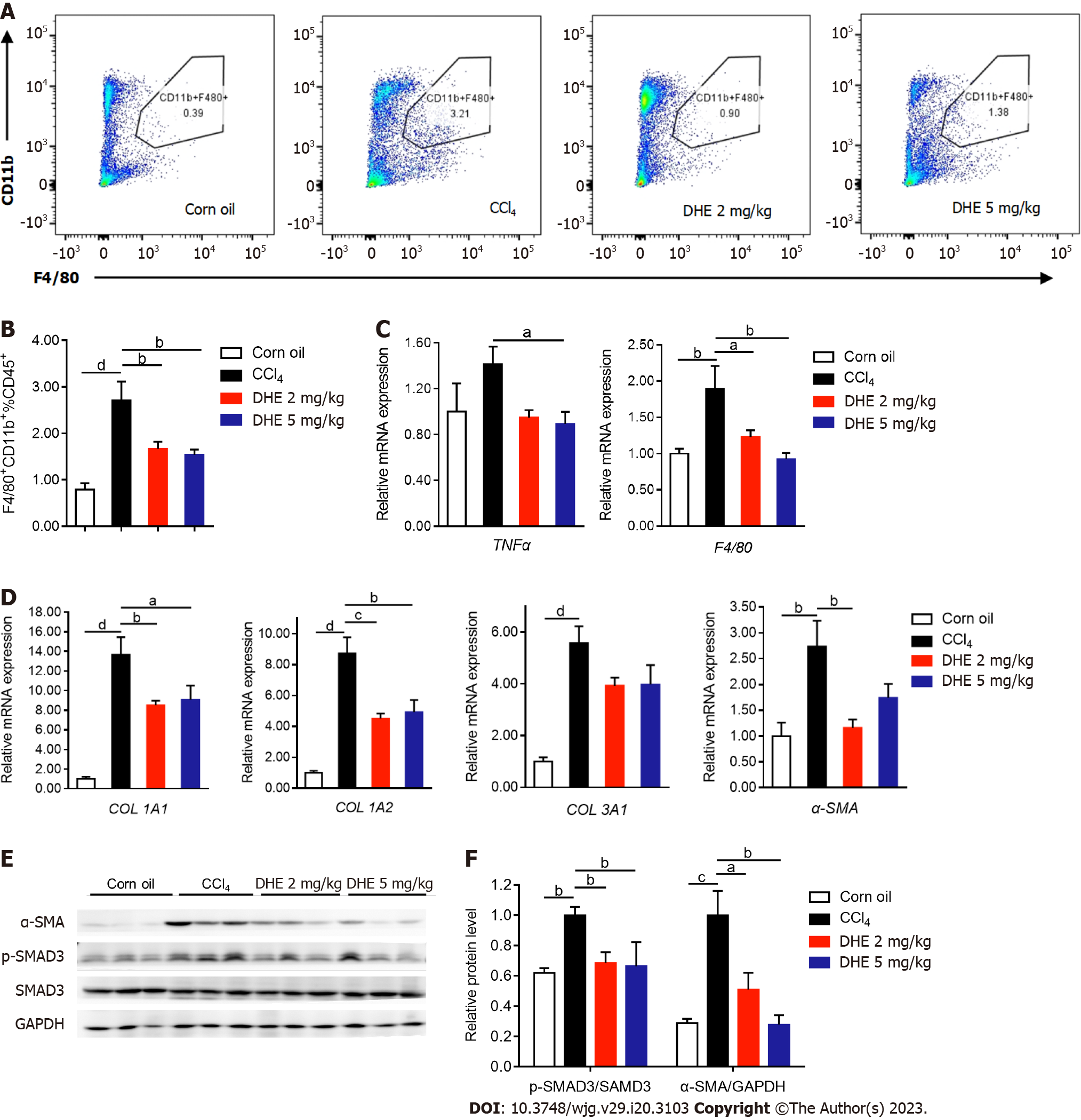
Figure 5 Dihydroergotamine decreased the inflammatory infiltration of macrophages and extracellular matrix deposition in the liver.
A and B: The flow cytometric analysis of CD11b+ cells (n = 6-8); C: The effects of dihydroergotamine (DHE) treatment on the mRNA expression levels of inflammation-related genes (n = 6-8); D: The effects of DHE treatment on the mRNA expression levels of extracellular matrix-related genes (n = 6-8); E: The protein levels of p-SMAD3 and α-SMA in liver tissues of mice in each group were detected by western blot (n = 3). All data are presented as means ± standard error of the mean. One-way ANOVA test was performed. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, and dP < 0.0001. TGFβ: Transforming growth factor β; TGFβR: Transforming growth factor β receptor; DHE: Dihydroergotamine.
- Citation: Zheng KX, Yuan SL, Dong M, Zhang HL, Jiang XX, Yan CL, Ye RC, Zhou HQ, Chen L, Jiang R, Cheng ZY, Zhang Z, Wang Q, Jin WZ, Xie W. Dihydroergotamine ameliorates liver fibrosis by targeting transforming growth factor β type II receptor. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(20): 3103-3118
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i20/3103.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3103