Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2023; 29(20): 3103-3118
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3103
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3103
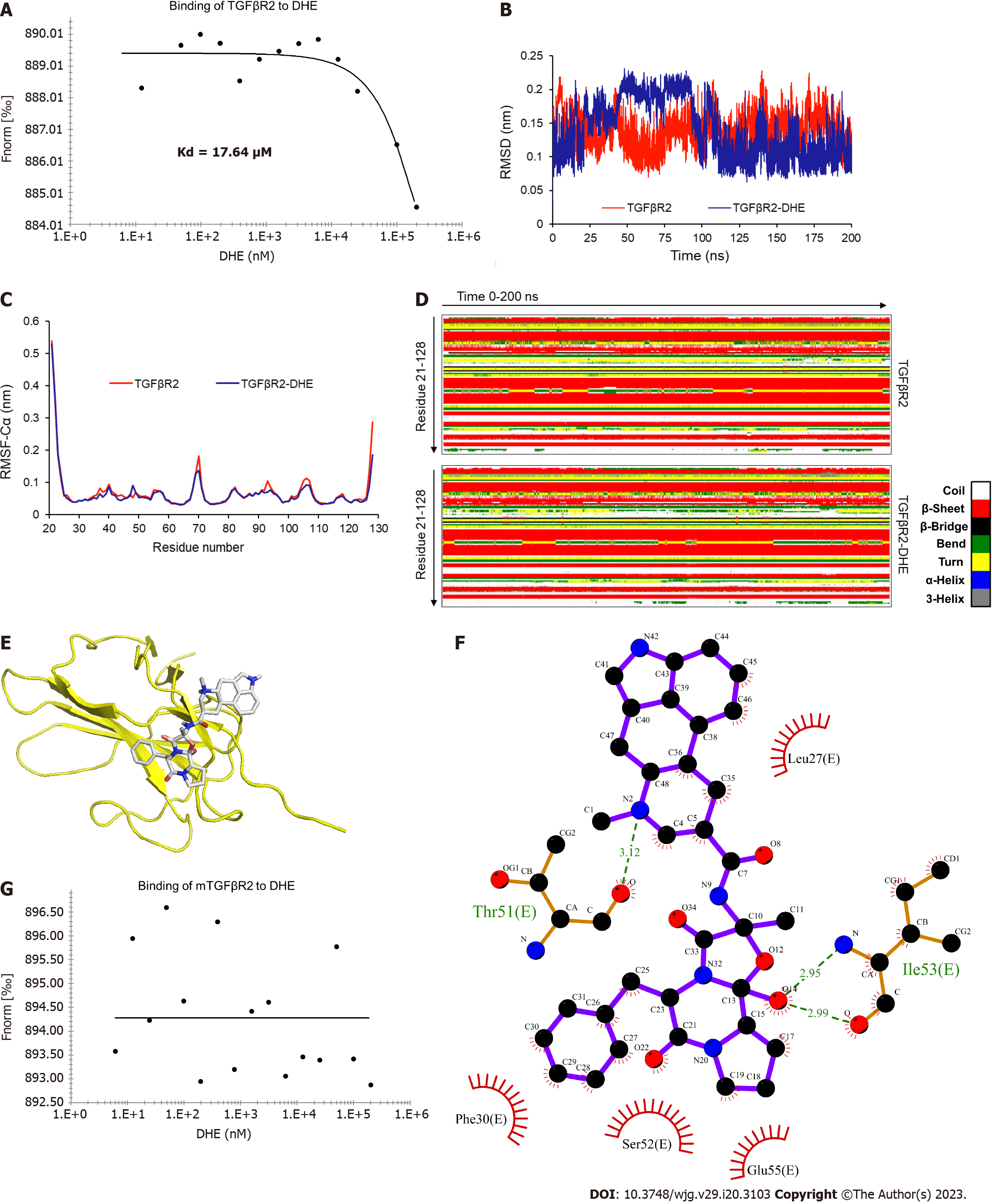
Figure 3 The binding affinity and sites of dihydroergotamine and transforming growth factor β type II receptor.
A: Transforming growth factor β type II receptor (TGFβR2) bound to dihydroergotamine (DHE) with a Kd of 17.64 μM; B: Molecular dynamics simulation results of DHE and TGFβR2. Root-mean-square deviation of TGFβR2 skeleton atom; C: Root-mean-square fluctuation of backbone Cα atoms of TGFβR2 skeleton atom; D: The secondary structure components of TGFβR2 and complex simulation systems in 0-200 ns; E and F: The binding sites of DHE and TGFβR2; G: The binding affinity of TGFβR2 mutants with DHE. TGFβ: Transforming growth factor β; TGFβR: Transforming growth factor β receptor; DHE: Dihydroergotamine.
- Citation: Zheng KX, Yuan SL, Dong M, Zhang HL, Jiang XX, Yan CL, Ye RC, Zhou HQ, Chen L, Jiang R, Cheng ZY, Zhang Z, Wang Q, Jin WZ, Xie W. Dihydroergotamine ameliorates liver fibrosis by targeting transforming growth factor β type II receptor. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(20): 3103-3118
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i20/3103.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3103