Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2023; 29(20): 3103-3118
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3103
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3103
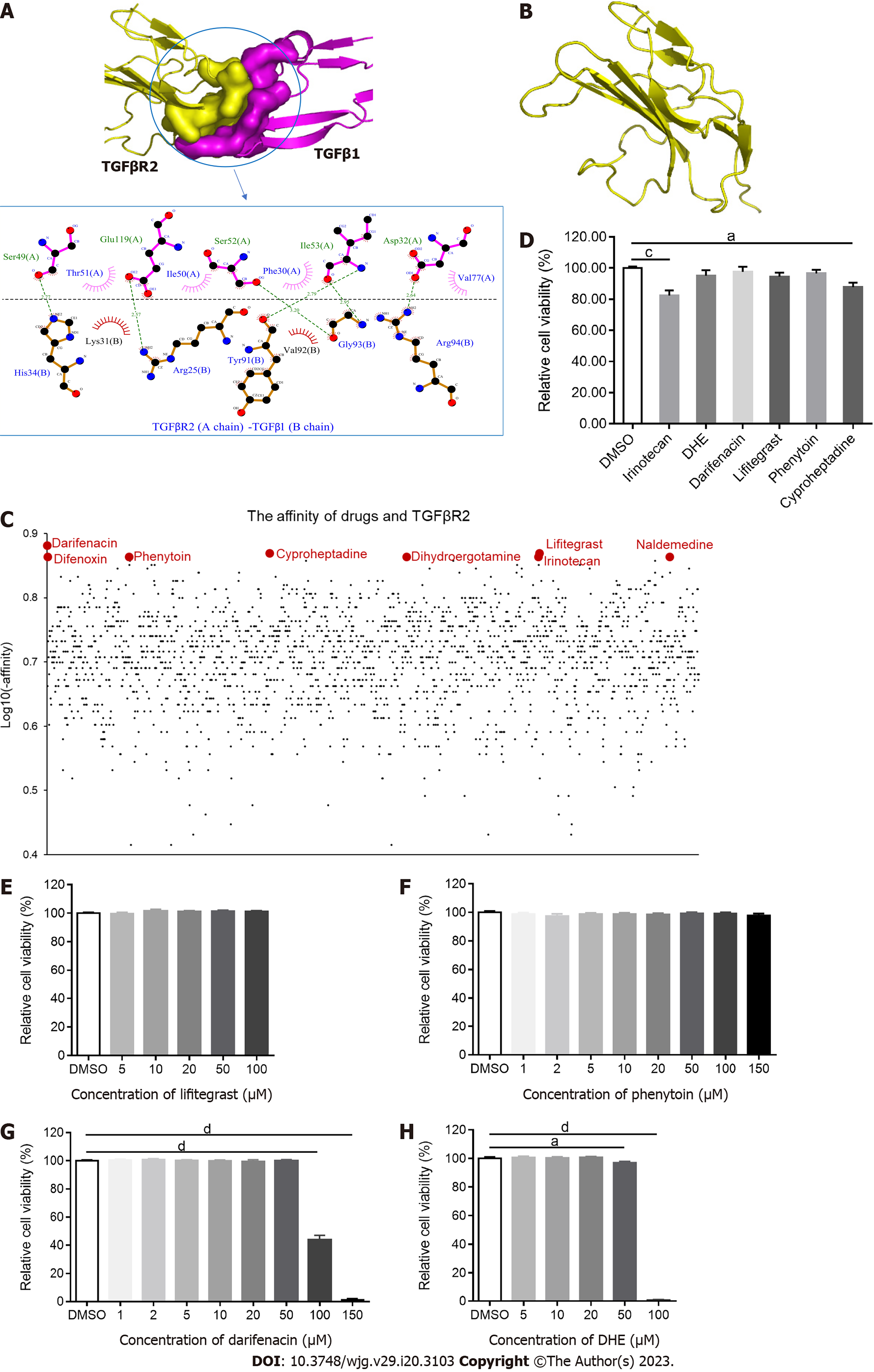
Figure 1 Screening Food and Drug Administration-approved drugs for binding to transforming growth factor β type II receptor.
A: The combination of transforming growth factor β type II receptor (TGFβR2) and transforming growth factor β 1 (TGFβ1); B: The structure of TGFβR2; C: The affinity of each Food and Drug Administration-approved drug and TGFβR2. The affinity of TGFβR2 and darifenacin, cyproheptadine, lifitegrast, difenoxin, phenytoin, dihydroergotamine (DHE), naldemedine, and irinotecan was -7.6, -7.4, -7.4, -7.3, -7.3, -7.3, -7.3, and -7.3 kcal/mol, respectively; D: Cell viability of LX-2 treated with 20 μM of the drugs for 24 h (n = 5); E-H: Cell viability following LX-2 treatment with different concentrations of darifenacin, DHE, lifitegrast, and phenytoin for 24 h (n = 6). All data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. One-way ANOVA test was performed. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, and dP < 0.0001. TGFβ: Transforming growth factor β; TGFβR: Transforming growth factor β receptor; DHE: Dihydroergotamine.
- Citation: Zheng KX, Yuan SL, Dong M, Zhang HL, Jiang XX, Yan CL, Ye RC, Zhou HQ, Chen L, Jiang R, Cheng ZY, Zhang Z, Wang Q, Jin WZ, Xie W. Dihydroergotamine ameliorates liver fibrosis by targeting transforming growth factor β type II receptor. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(20): 3103-3118
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i20/3103.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3103