Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2023; 29(20): 3084-3102
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3084
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3084
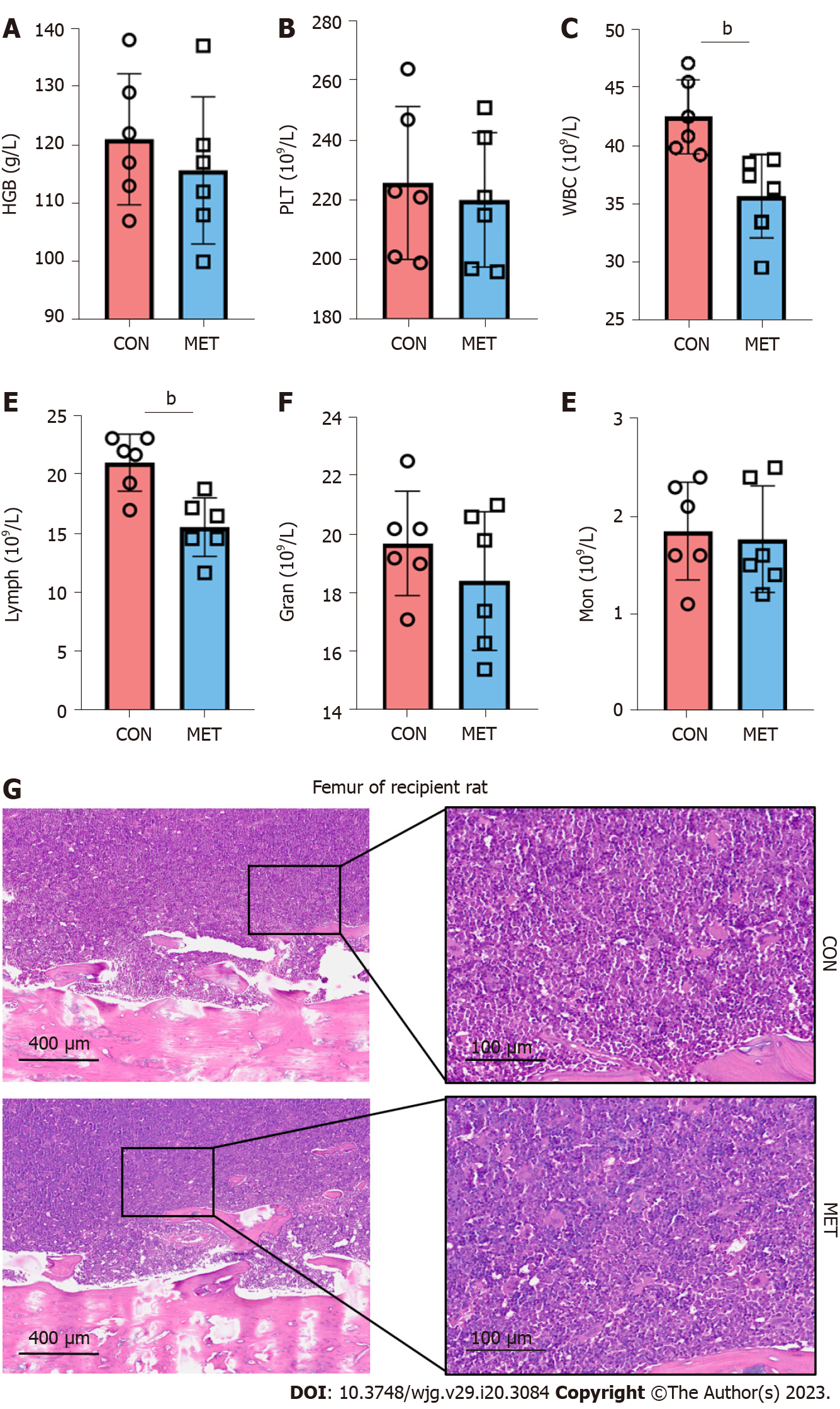
Figure 1 Metronomic capecitabine showed no significant myelosuppression.
A and B: Hemoglobin level and platelets count in the peripheral blood; C-F: White blood cells, lymphocytes, granulocytes, and monocytes counts in the peripheral blood; G: Bone marrow tissue was stained with hematoxylin and eosin (50 × and 200 ×). Statistical analysis was done by unpaired t-test, n = 6. Data are shown as mean ± SD; bP < 0.01 vs the control group. CON: Untreated control groups, rats received 0.9% normal saline for 7 d; MET: Metronomic capecitabine (CAP)-treated groups, rats received metronomic CAP (100 mg/kg/d) treated for 7 d; HGB: Hemoglobin; PLT: Platelets; WBC: White blood cells; lymph: Lymphocytes; Gran: Granulocytes; Mon: Monocytes.
- Citation: Wang H, Wang ZL, Zhang S, Kong DJ, Yang RN, Cao L, Wang JX, Yoshida S, Song ZL, Liu T, Fan SL, Ren JS, Li JH, Shen ZY, Zheng H. Metronomic capecitabine inhibits liver transplant rejection in rats by triggering recipients’ T cell ferroptosis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(20): 3084-3102
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i20/3084.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3084