Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2023; 29(2): 367-377
Published online Jan 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i2.367
Published online Jan 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i2.367
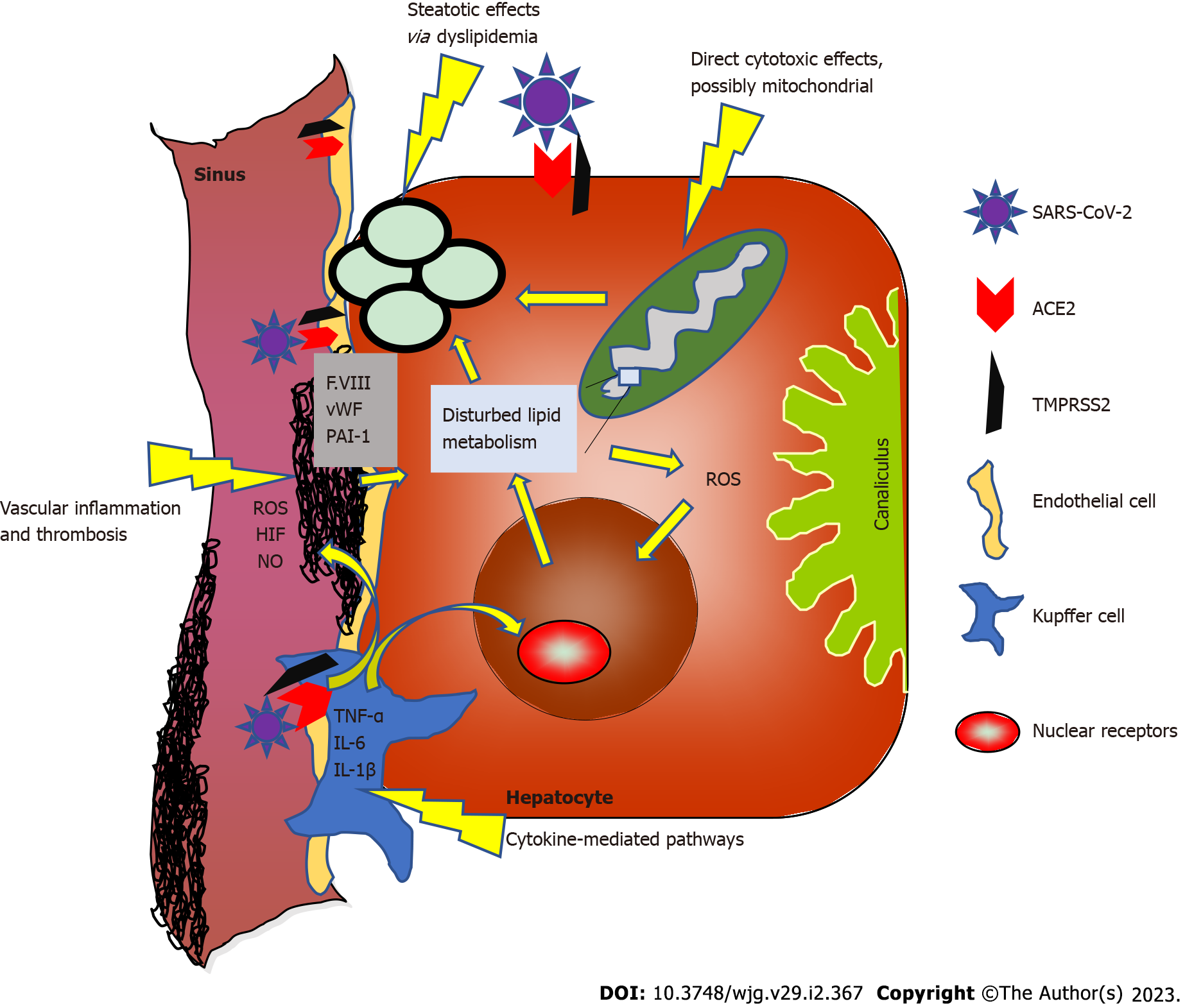
Figure 1 Possible mechanisms of coronavirus disease-induced liver injury and the interplay between molecular pathways of inflammation in both diseases (in pre-existing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease).
F. VIII: Factor VIII; vWF: von Willebrand factor; HIF: Hypoxemia-inducible factor; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; IL-6: Interleukin-6; NO: Nitric oxide; PAI-1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2; ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme-2; TMPRSS2: Transmembrane serine protease 2.
- Citation: Dietrich CG, Geier A, Merle U. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and COVID-19: Harmless companions or disease intensifier? World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(2): 367-377
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i2/367.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i2.367