Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2023; 29(19): 2905-2915
Published online May 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i19.2905
Published online May 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i19.2905
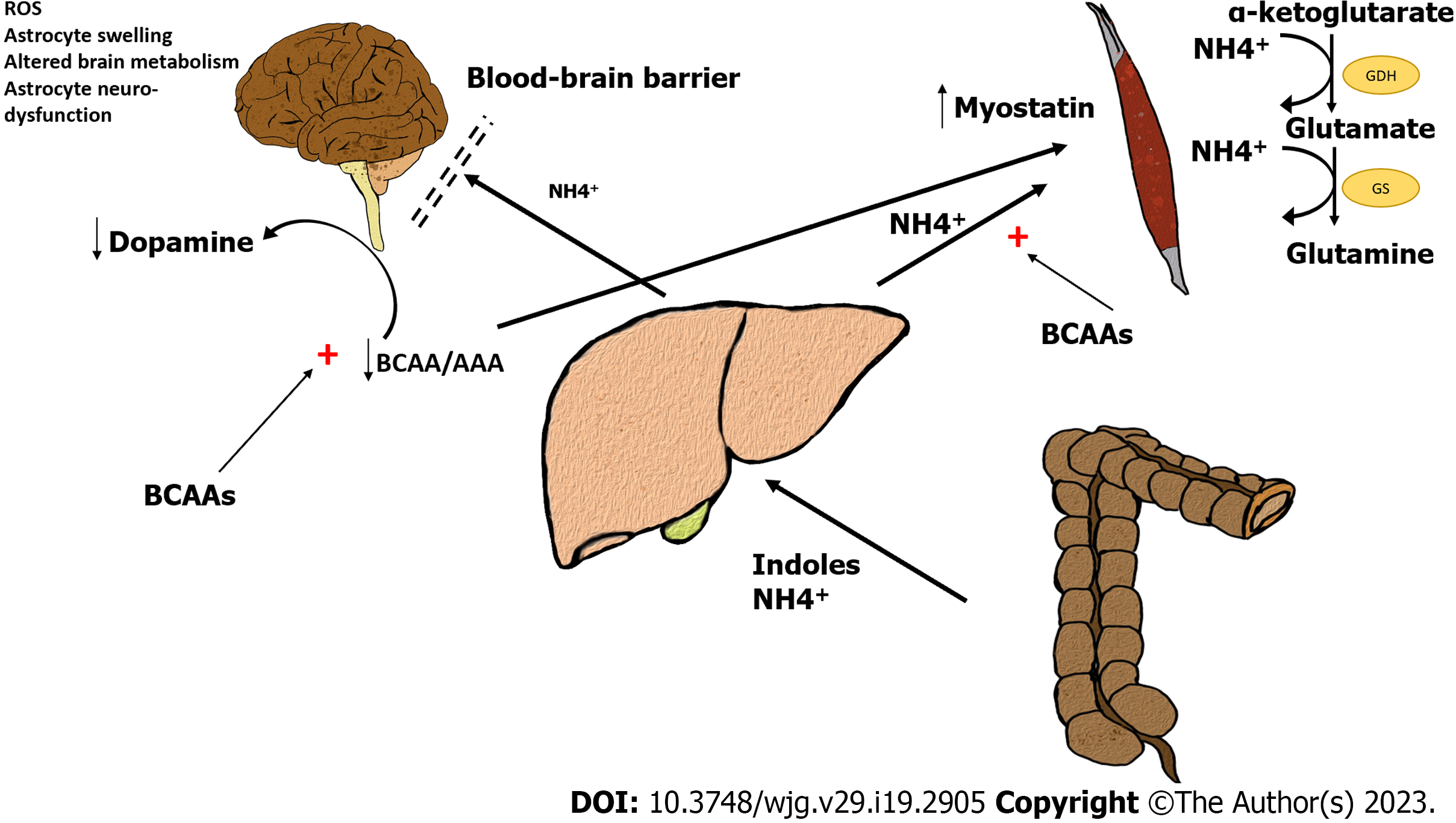
Figure 1 Gut derived ammonia and other aromatic compounds pass into the systemic circulation due to reduced liver function and the presence of porto-systemic shunts.
A low plasma branched chain amino acids (BCAA)/aromatic amino acids (AAA) ratio has been observed in liver cirrhosis. BCAA and AAA compete for the same transporter at blood-brain barrier. The increased availability of AAA causes an increase in aromatic neurotransmitter precursors resulting in a false dopaminergic transmission and a reduction in dopamine synthesis. At brain level, ammonia causes astrocyte metabolism changes including reactive oxygen species increase, altered glucose and protein metabolism and astrocyte swelling, resulting in altered neurotransmission. Muscle is a key site of ammonia detoxification by means of the sequential action of glutamate dehydrogenase and glutamine synthetase. Ammonia increases myostatin expression, thus resulting in reduced protein synthesis and inhibition of myogenesis. The administration of BCAAs can increase muscle ammonia uptake from blood and can interfere with amino acids pass throughout the blood brain barrier with beneficial effects on both hepatic encephalopathy and sarcopenia. BCAAs: Branched chain amino acids; AAA: Aromatic amino acids; NH4+: Ammonia; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; GDH: Glutamate dehydrogenase; GS: Glutamine synthetase.
- Citation: Marrone G, Serra A, Miele L, Biolato M, Liguori A, Grieco A, Gasbarrini A. Branched chain amino acids in hepatic encephalopathy and sarcopenia in liver cirrhosis: Evidence and uncertainties. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(19): 2905-2915
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i19/2905.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i19.2905