Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2023; 29(18): 2875-2887
Published online May 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i18.2875
Published online May 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i18.2875
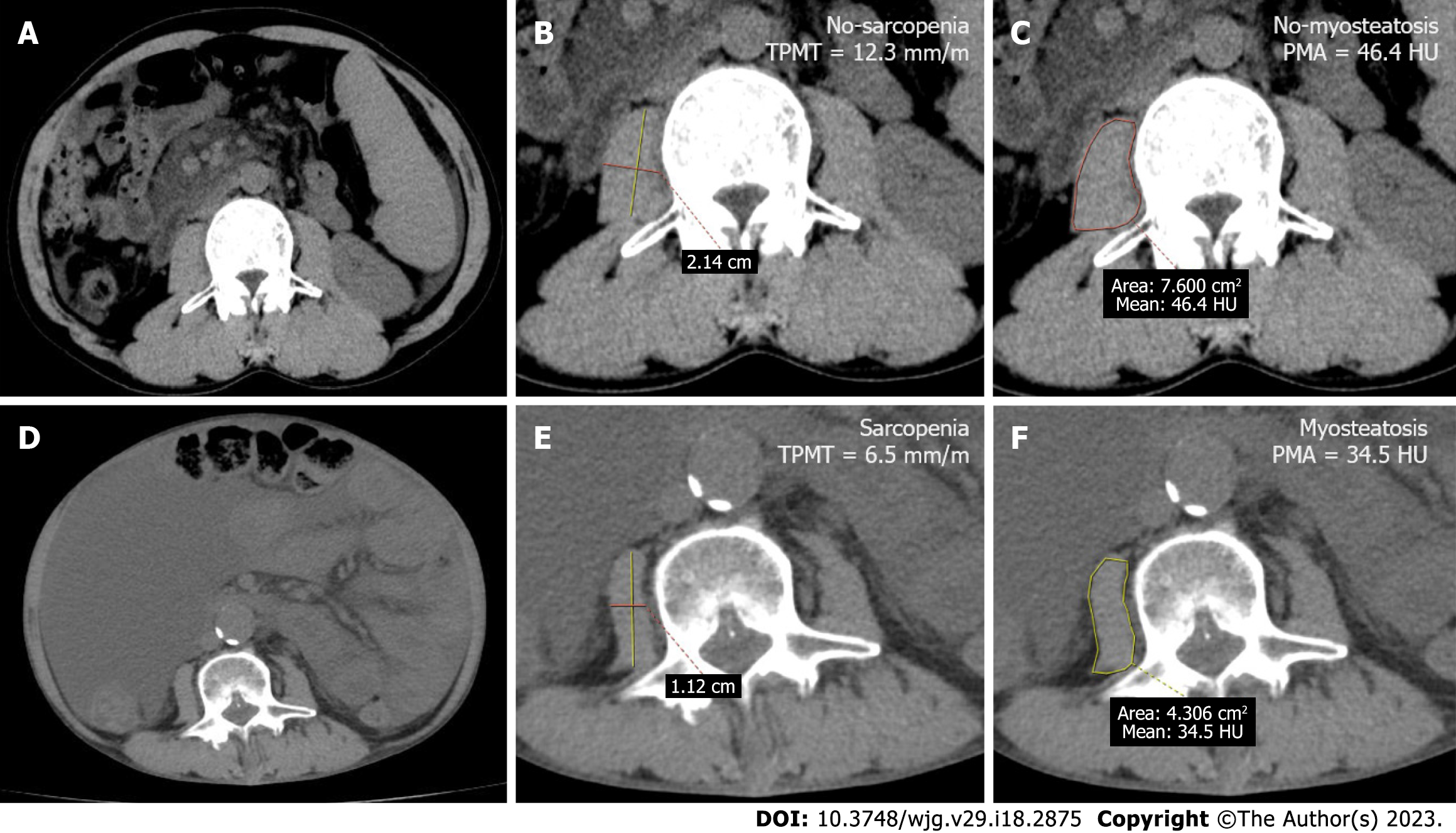
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography images at the level of the third lumbar vertebrae were used to measure the transversal psoas muscle thickness and psoas muscle attenuation in a 45-year-old man without sarcopenia and myosteatosis, and a 51-year-old man with sarcopenia and myosteatosis.
A: The axial computed tomography (CT) scan image of a 45-year-old cirrhotic patient (height: 1.74 m, weight: 74 kg) who developed variceal rebleeding; B and C: The patient had normal transversal psoas muscle thickness (TPMT) and psoas muscle attenuation (PMA) levels: 12.3 mm/m (21.4 mm/1.74 m) and 46.4 HU, respectively; D-F: The axial CT scan image of a 51-year-old cirrhotic patient (height: 1.72 m, weight: 55 kg) who developed refractory ascites (D), and had low TPMT and PMA (6.5 mm/m [11.2 mm/1.72 m] and 34.5 HU) (E and F). TPMT: Transversal psoas muscle thickness.
- Citation: Yin L, Chu SL, Lv WF, Zhou CZ, Liu KC, Zhu YJ, Zhang WY, Wang CX, Zhang YH, Lu D, Cheng DL. Contributory roles of sarcopenia and myosteatosis in development of overt hepatic encephalopathy and mortality after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(18): 2875-2887
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i18/2875.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i18.2875