Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2023; 29(17): 2642-2656
Published online May 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2642
Published online May 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2642
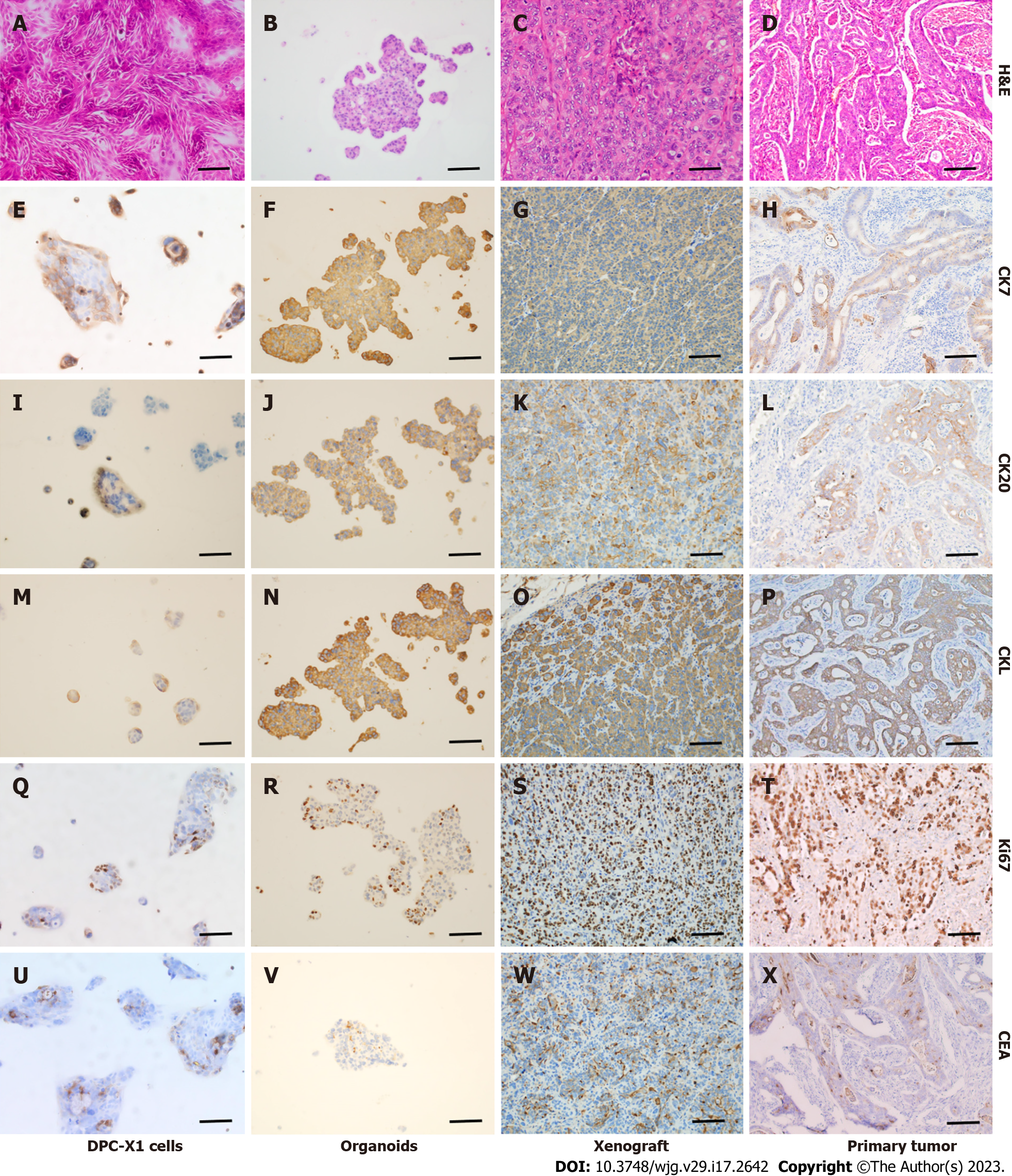
Figure 6 Hematoxylin and eosin and immunohistochemical staining of DPC-X1 cells, organoid, xenograft tumor, and primary tumor.
A-D: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of DPC-X1 cells, organoids, xenograft tumor, and primary tumor; E-H: Strong cytokeratin (CK)7 positive staining of DPC-X1 cells, organoids, xenograft tumor, and primary tumor; I-L: Strong CK20 positive staining of DPC-X1 cells, organoids, xenograft tumor, and primary tumor; M-P: Strong cytokeratin low molecular weight positive staining of DPC-X1 cells, organoids, xenograft tumor, and primary tumor; Q-T: Ki67 staining of DPC-X1 cells, organoids, xenograft tumor, and primary tumor; U-X: Carcinoembryonic antigen focal staining of DPC-X1 cells, organoids, xenograft tumor, and primary tumor. Scale bars: 100 μm. H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; CK7: Cytokeratin 7; CK20: Cytokeratin 20; CKL: Cytokeratin low molecular weight; CEA: Carcinoembryonic antigen.
- Citation: Xu H, Chai CP, Miao X, Tang H, Hu JJ, Zhang H, Zhou WC. Establishment and characterization of a new human ampullary carcinoma cell line, DPC-X1. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(17): 2642-2656
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i17/2642.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2642