Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2023; 29(17): 2616-2627
Published online May 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2616
Published online May 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2616
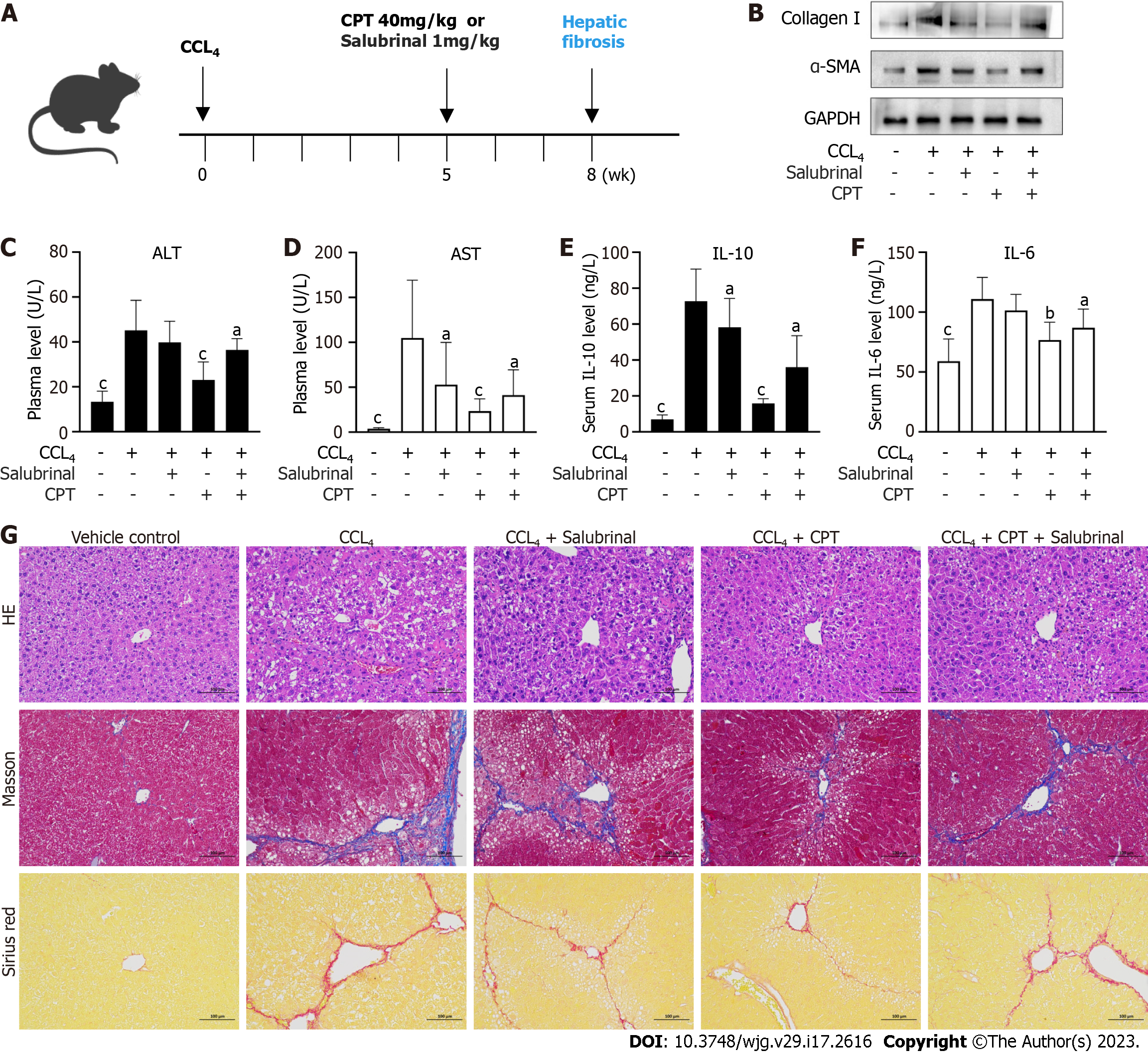
Figure 5 Cryptotanshinone protects the liver against carbon tetrachloride-induced injury and inflammation.
Cryptotanshinone (CPT) alleviates hepatic fibrotic injury in mice. Mice were injected with carbon tetrachloride (CCL4) for 8 wk to induce liver fibrosis. During weeks 5 through 8, mice in the treatment groups were given CPT (40 mg/kg) or salubrinal (1 mg/kg). A: CPT treatment protocol in the CCL4-induced hepatic fibrosis mouse model; B: Western blot analysis of α-SMA and collagen I in the liver tissue; C: Determination of serum alanine aminotransferase levels; D: Determination of serum aspartate aminotransferase levels; E: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) measurement of IL-6 levels in the serum; F: ELISA measurement of IL-10 levels in the serum; G: Liver sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, Masson reagents, and Sirius red. Scale baes: 100 μm. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 compared with the CCL4 group. CPT: Cryptotanshinone; CCL4: Carbon tetrachloride.
- Citation: Hou XX, Li YW, Song JL, Zhang W, Liu R, Yuan H, Feng TT, Jiang ZY, Li WT, Zhu CL. Cryptotanshinone induces apoptosis of activated hepatic stellate cells via modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(17): 2616-2627
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i17/2616.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2616