Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2023; 29(17): 2616-2627
Published online May 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2616
Published online May 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2616
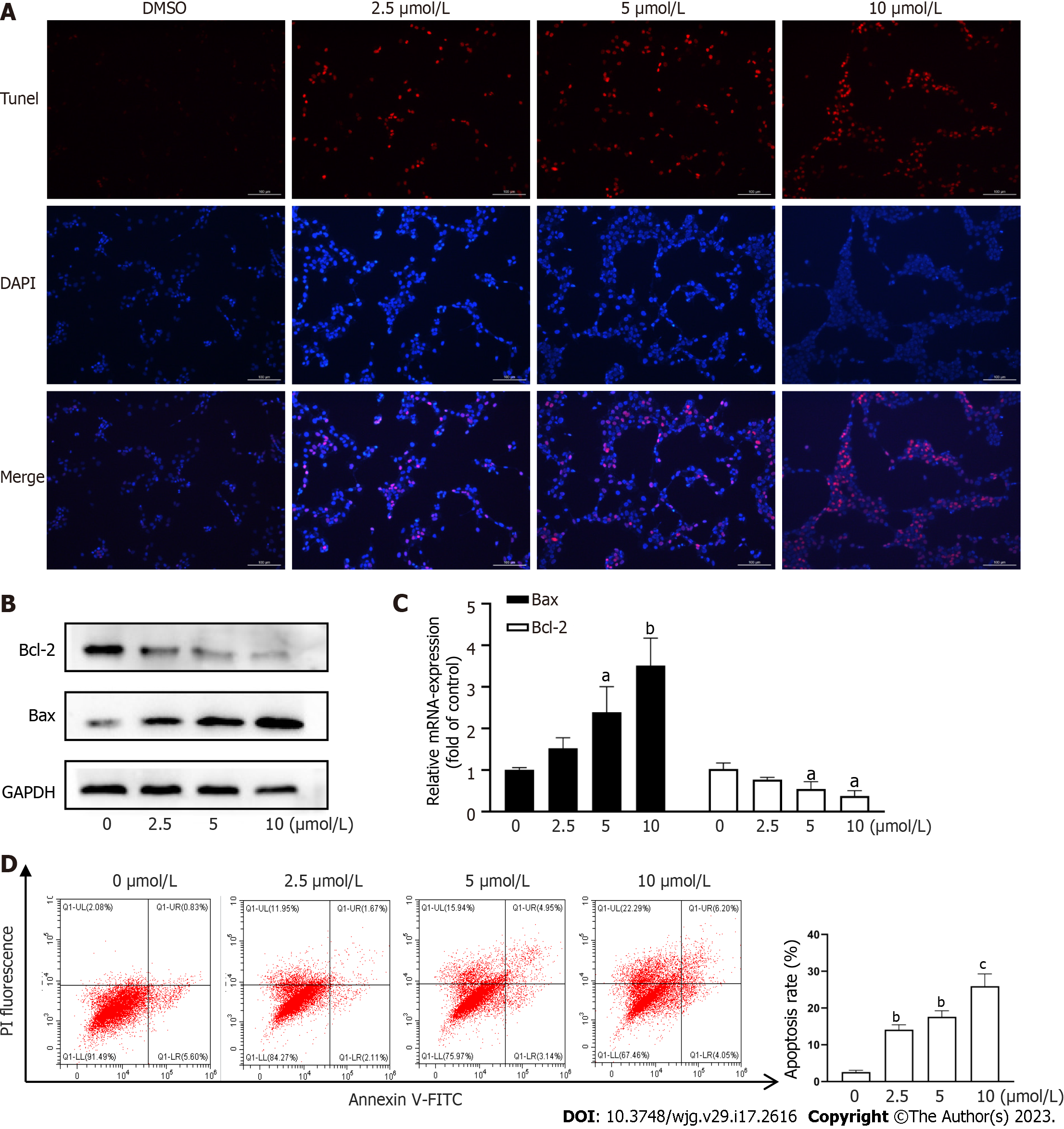
Figure 2 Cryptotanshinone induces apoptosis of activated hepatic stellate cells.
A: TUNEL staining to assess LX2 apoptosis. Red fluorescence indicates apoptotic cells. Scale baes: 100μm; B: Western blot analysis of Bcl-2 and Bax protein expression in LX2 cells; C: Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis of Bcl-2 and Bax mRNA levels in LX2 cells; D: Flow cytometric analysis of LX2 cell apoptosis using fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled Annexin-V/propidium iodide staining. Cells located in the right two quadrants of each figure were considered apoptotic cells. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 versus control.
- Citation: Hou XX, Li YW, Song JL, Zhang W, Liu R, Yuan H, Feng TT, Jiang ZY, Li WT, Zhu CL. Cryptotanshinone induces apoptosis of activated hepatic stellate cells via modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(17): 2616-2627
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i17/2616.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i17.2616