Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2023; 29(16): 2397-2432
Published online Apr 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2397
Published online Apr 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2397
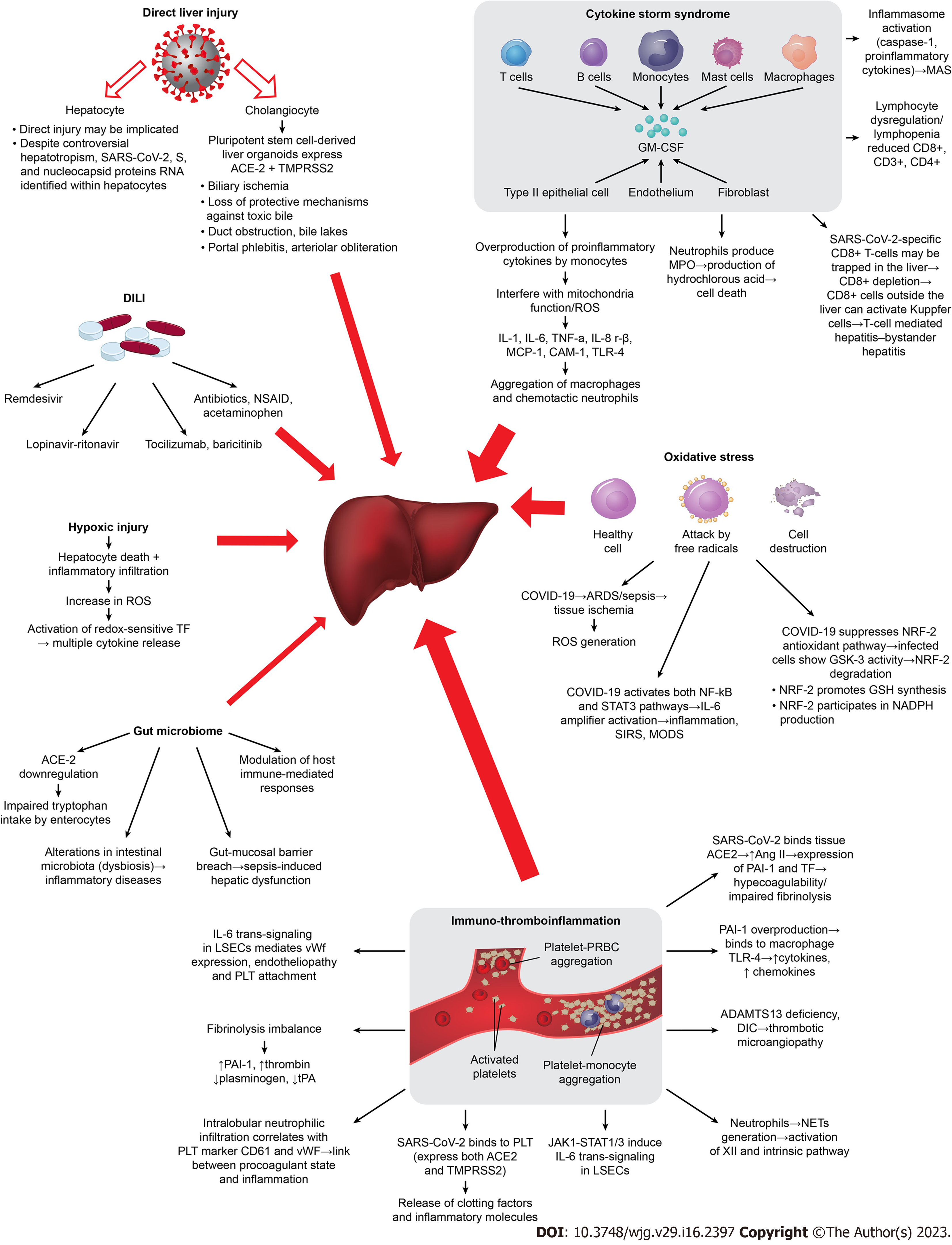
Figure 1 Mechanisms implicated in COVID-19-induced liver injury.
The different width of the red arrows represents the different contribution/significance of each separate mechanism in coronavirus disease 2019-associated liver injury. ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme-2; ADAMTS 13: A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with a thrombospondin type 1 motif; Ang II: Angiotensin II; ARDS: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; CAM-1: Cell-adhension molecule-1; DIC: Disseminated intravascular coagulation; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; GSK: Conserved serine/threonine kinase; IL: Interleukin; JAK1: Janus kinase 1; LSECs: Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; MAS: Macrophage activation syndrome; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; MCP-1: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1; NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NETS: Neutrophil extracellular traps; NRF2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; NSAIDS: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; PAI-1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; PLT: Platelet; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TF: Tissue factor; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; TMPRSS2: Transmembrane serine protease-2; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; TPA: Tissue plasminogen activator; vWF: Von Willebrand factor; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
- Citation: Liatsos GD. SARS-CoV-2 induced liver injury: Incidence, risk factors, impact on COVID-19 severity and prognosis in different population groups. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(16): 2397-2432
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i16/2397.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2397