Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2023; 29(15): 2294-2309
Published online Apr 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2294
Published online Apr 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2294
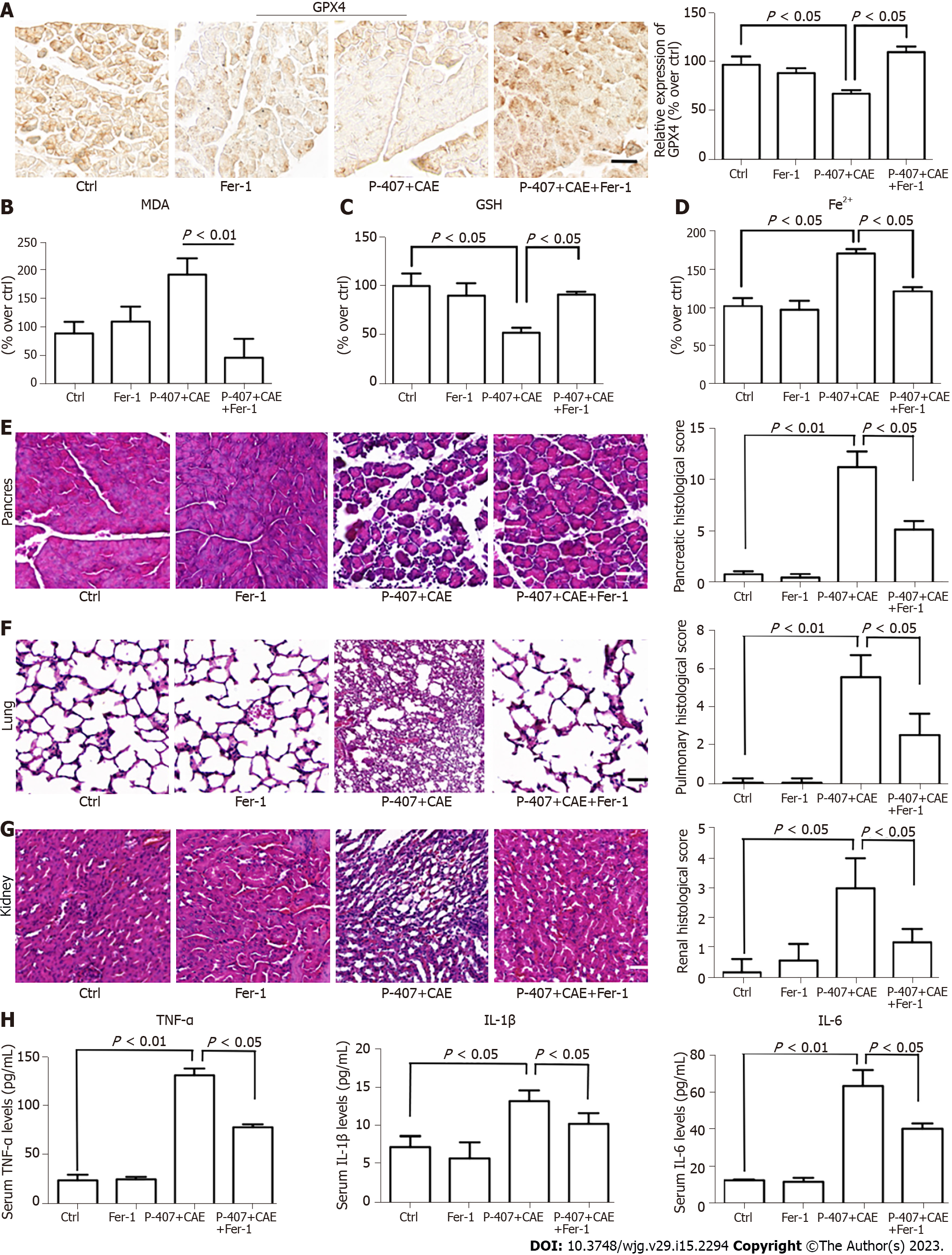
Figure 4 The inhibition of ferroptosis attenuated P-407 + Caerulein-induced hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis in mice (n = 4).
A: Immunohistochemistry for Glutathione peroxidase 4 in the pancreas tissues of the P-407 + Caerulein (CAE) and P-407 + CAE + Ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1) groups; B: The malonaldehyde levels; C: The glutathione levels; D: Fe2+ levels in pancreases of P-407 + CAE and P-407 + CAE + Fer-1 groups; E: Hematoxylin–eosin (HE) staining and histological scores of the pancreas; F: HE staining and histological scores of the lung; G: HE staining and histological scores of the kidney; H: Serum tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6 levels of the P-407 + CAE and P-407 + CAE + Fer-1 groups. NOX: NADPH oxidase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; CAE: Caerulein; MDA: Malonaldehyde; Fer-1: Ferrostatin-1; GSH: Glutathione; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Meng YT, Zhou Y, Han PY, Ren HB. Ferroptosis inhibition attenuates inflammatory response in mice with acute hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(15): 2294-2309
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i15/2294.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i15.2294